Caffeine VS Drug Abuse: Could They Trigger A Kidney Stone Crisis?
Grade 8
Presentation
Problem
The problem that I am going to be researching is: "How does the consumption of caffeine or addictive substances affect kidney stone formation?"
Over millions of teens and young adults struggle with drinking problems or are chronically consuming caffeinated food and beverages to help them cope with stress, lack of energy or even just temptations or pleasure. This can be highly associated with kidney stones, affecting over 600,000 young adults each year in the U.S alone.
This study aims to investigate how these substances can influence mineral excursion, calcium imbalances, hydration levels and many others that contribute to kidney stone formation. By analyzing these factors, it can help us all try our best to refrain from a disease as painful as kidney stones by modifying our lifestyle and diet to allow healthier alternatives to caffeine and addictive substances.
Method
This research study aims to investigate how caffeine and addictive substances affect kidney stone formation. To do this, I chose a variety of different caffeinated/addictive substances and analyzed their effects on urine pH levels, oxidative stress, hydration factors and many more!
To ensure that my data is accurate, I will collect information about caffeine in both solid and liquid forms and similarly, I will collect information about addictive substances in both gateway and illicit forms. For caffeine, I conducted research on: Nescafe Iced Coffee, Monster Energy Drinks and President's Choice Granola Bars. And for addictive substances, I chose alcohol and nicotine as my gateway substances and MDMA/Ecstasy and cocaine as my illicit substances.
In the end I will not only compare and contrast each variable, I will also conduct a research of each consumed product and their effects on kidney stone formation by researching their scientific processes and by seeking insights from a professional, Dr. Maham Zehra, a Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS) with 1 year of experience.
I will also conduct a verbal interview with Akbar Rais, an individual who had been diagnosed with kidney stones in November 2022. Akbar Rais provided valuable insights by answering certain inquiries on his experiences with kidney stones.
This study will also incorporate background information like "How do Kidney stones Affect Kidney Function?" which explores ideas such as calcium excursion and oxidative stress, which will later tie into our main focal point, how does the consumption of caffeine or addictive substances affect kidney stone formation?
Research
Hypothesis
If you consume large amounts of caffeine or addictive substances then you are more likely to develop kidney stones in your urinary tract because as a diuretic, chronic caffeine consumption can increase calcium excursion in the urine by as much as 77%. As for addictive substances, Chronic consumption of substances can impair function in the liver, the heart and most importantly the kidneys by increasing waste excursion and potentially narrowing the blood vessels creating an environment for kidney stones to form.
Furthermore, in regards to my comparison between caffeinated goods such as Nescafe Iced Coffee, Monster Energy drinks and President's Choice Granola Bars, I hypothesize that Monster Energy drinks will be the greatest risk factor for kidney stone formation due to its excessive amounts of sugar and caffeine additives as they may increase calcium excursion in the urine or make worse kidney impairments. And that President’s Choice Granola Bars will be the lowest risk factor as they may be a good source of micronutrients and energy.
As for addictive substances I hypothesize that for the illicit substances (MDMA and Cocaine), Cocaine will be the greatest risk factor due to its link with bone resorption and other health disadvantages and for gateway substances (Alcohol and nicotine), Alcohol will be the greatest risk factor due to its impact on the liver and link with oxalate excursion.
And finally, I hypothesize that Addictive substances will have a slightly greater impact on kidney stone formation in comparison to caffeine because of their increasing health disadvantages and disliked demeanor of consumption by healthcare professionals for any age group. Additionally, I think Illicit drugs also have a greater impact on kidney stone formation rather than gateway drugs due to their more long lasting effects and health concerns.
What is a Kidney Stone?
Kidney stones, also known as renal calculi or nephrolithiasis, are hard, solid masses formed from clusters of tiny particles in urine. These stones can develop in one or both kidneys (unilateral or bilateral) and vary significantly in size, color, and texture. Typically yellow or brown, they can range from the size of a tiny pebble or a small pea to, in rare cases, as large as a golf ball. Depending on its environmental factors and conditions, kidney stones can have smooth surfaces or jagged edges. Furthermore, kidney stones typically form in the renal pelvis, a gland in the inner lining of the kidney, particularly at the point where urine transitions from the kidney tissue into the urinary collecting system. This area provides an environment where minerals and waste products in urine can crystallize and begin to accumulate, eventually forming stones.
How Are Kidney Stones Formed?
Formation of kidney stones begin from substances such as: calcium, oxalate, and uric acid, the key components of the urine in our body. However, these substances can become out of balance and can lead to higher concentration of solutes (such as calcium, oxalate, etc.) than there is solvent (water), creating a condition known as supersaturation. This high concentration allows the substances to crystallize, initiating a process known as nucleation, where dozens of crystal particles stick together to form a stone. Overtime, the crystal particles build up and grow into larger stones. Furthermore, kidney stones develop when the urine becomes concentrated, creating an environment where crystallization is more likely to occur. Kidney stones may cause discomfort or excruciating pain as they exit the interior surface of the kidney, move through the ureter and enter the urinary tract triggering pain due to pressure and tissue irritation.
What is the relationship between caffeine and kidney stones?
What is Caffeine?
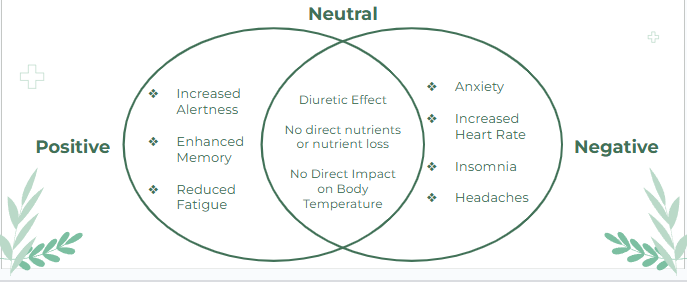
Caffeine is a stimulant, meaning it can increase energy in the nervous system and in the brain by 10-50% (exact percentage depends on different factors). But whether that energy is increased in positive ways or negative ways may vary, as consuming caffeine in small amounts can help with refreshment and attentiveness while consuming larger doses can generate anxiety or insomnia. It is a common misconception that caffeine can only be found in coffee, however that is not actually the case. Caffeine can also be found in substances such as tea, cocoa, energy drinks, soft drinks and even energy bars.
How does Caffeine affect the body?
What is the relationship between caffeine and kidney disease?
“Because coffee has diuretic properties (meaning it may cause you to pee more often), people often assume that drinking coffee may be dehydrating, thus increasing your risk for kidney stones. However, recent research on kidney stones shows that the use of caffeine may actually prevent kidney stones.”
- Dr. Maham Zehra
Interesting enough, caffeine intake can actually reduce the odds of kidney diseases such as kidney stones by 40%. This is because, as a chemical, caffeine is a diuretic, meaning it increases the amount of urine your body produces, diluting the amount of stone producing minerals (calcium, oxalate, and uric acid). However, that increase of production can also increase the amount of urinary solutes. This depends on 3 factors: the individual, the type of caffeine beverage consumed and hydration levels. Here is how:
The Individual
While caffeine intake can usually reduce the rate of kidney stone formation on the average person, for an individual prone to kidney stones (by genetics, demographic factors, medical conditions etc), it is not always the same case. This is because, for certain individuals, caffeine can increase calcium levels or in medical terms, hypercalciuria, leading to the most common type of kidney stone, calcium oxalate.
Type of Caffeinated Beverage Consumed
"Caffeine consumption cannot always harm the kidney if taken in moderation. It also depends on a person’s metabolism. Some studies show that caffeine intake helps prevent Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) while others say that it can cause kidney stones. On the other hand, it is important to know that kidney stones are mainly formed by Calcium Oxalate. And Coffee is a main source of Calcium Oxalate which can contribute to kidney stones. People with kidney stones should consider coffee to be a possible risk factor."
- Dr. Maham Zehra
Nescafe Iced Coffee
While general coffee poses an increased risk of kidney stones by dehydration factors and by increasing urine production, iced coffee is sometimes made with other additives like milk, ice cream or creamers which can increase calcium excursion, blood sugar and sometimes oxalate levels. Nescafe Iced coffee also contains 75 mg of potassium, which also plays a role in kidney function. Potassium citrate helps prevent kidney stones by binding with calcium in the gut before entering the kidneys. However, the potassium in Nescafe Iced Coffee is potassium chloride which does not offer the same protective benefits, and instead, can potentially alkalize urine pH levels making a more favorable space for uric acid and calcium oxalate stones to form. However, these effects would be more significant in individuals with kidney disease as for most people, potassium in coffee is not a major issue.
Monster Energy Drinks
The average Monster Energy Drink contains relatively unsafe levels of ingredients assisting with kidney stone development. For instance, one can holds about 137-166 mg of caffeine which as a diuretic, increases urine production leading to dehydration and solute concentration in the urine. But caffeine isn’t the only problem, some Monster Energy Drinks contain about 54g of sugar which is more than 12 ½ teaspoons! This alarming concentration of sugar can rapidly increase blood sugar levels also increasing urine production. Furthermore, Monster Energy Drinks also contain sodium levels reaching as high as 370 mg, that is 15-25% of the amount you should have in an entire day! Studies also show that 11-61% of increasing kidney stone cases are because of excessive sodium intake. This is because of its nature to cause the kidneys to excrete unsafe levels of calcium in the urine. And lastly, Zero Sugar Monster Energy Drinks also contain artificial sweeteners in the form of sucralose to act as a sugar substitute. These sweeteners usually go under the category of oxalates and contribute to kidney stones when combined with calcium, forming mostly calcium oxalate kidney stones.
President's Choice Granola Bars
President’s Choice Granola Bars contain high amounts of oxalates, sodium and sugar making them highly contributory to kidney stone formation. To start, President’s Choice Granola Bars contain large amounts of oxalate in the form of dark chocolate chips which are made with cocoa butter and unsweetened chocolate. These ingredients can then bind with calcium in the kidneys to form calcium oxalate stones. Secondly, sugar content. President's Choice Granola Bars contain a considerable amount of sugar, honey, glucose, fructose, vanilla extract and fancy molasses; all sweeteners with the ability to increase calcium excursion and fructose with the ability to increase levels of uric acid. Furthermore, President’s Choice Granola bars contain 45 mg of sodium which while is a negligible amount, if consumed regularly without adequate water intake, can contribute to calcium excursion and in worse cases kidney stone development.
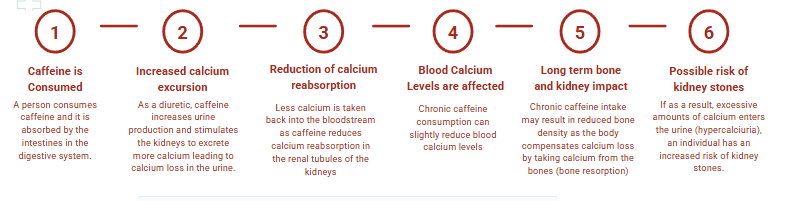
How does Caffeine increase Calcium in the urine?
A heavy increase of urinary solutes, such as calcium can be a subsequent cause to forming kidney stones. Caffeine can actually do just that, increasing calcium clearance by as much as 77%. Calcium clearance refers to the rate at which the kidney filters caffeine from the bloodstream and brings it into the urine. The graph below explains the process of how caffeine affects calcium clearance:
Hydration Levels
While caffeine is a diuretic, it is made up of 95% water making its diuretic effects significantly low. This means caffeine can cause mild effects on dehydration making it negligible to the formation of kidney stones. However, the build up of these “low” dehydration factors can still contribute to the concentration of urine increasing stone risk.
How does Caffeine increase the risk of Calcium Oxalate stones?
As explained in the previous diagrams, caffeine can cause mild dehydration and can contribute to an increase of calcium excursion. But what if I was to tell you that these factors contribute most to calcium oxalate stones? While other kidney stones are formed by factors such as high protein diets or UTIs, calcium oxalate stones are formed mostly by dehydration and excessive urine build up, making an individual with high caffeine intake more prone to them.
How does Caffeine influence urine acidity or alkalinity?
While caffeine does not significantly alter urine pH levels, a neighboring factor such as the type of caffeinated substance can subsequently lead to a range of different urine pH levels. For instance, coffees and teas contain organic acids like chlorogenic acids contributing to acidic or low pH levels while beverages like Monster Energy drinks contain inorganic additives such as sodium bicarbonate, known to cause alkaline or high pH levels in the urine.
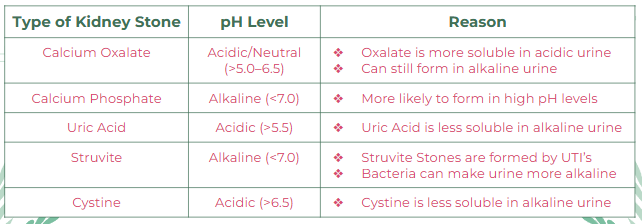
How does urine acidity or alkalinity affect kidney stone formation?
Kidney stones form in an environment made up of mostly urine, making them strongly impacted by urinary pH levels.
What is Substance Abuse?
Majority of people who consume drug substances consume them out of pleasure, as a coping mechanism or even just for amusement. However, they do not know the serious health risks that may come along with this dangerous consumption. Many addictive substances can lead to severe mental health disorders, organ damage, a severe buildup of intoxicants or in severe cases, heart disease, diabetes and even kidney dysfunction; all severe health conditions leading to complications or even death. While the short term effects may seem amusing and harmless, the short-term effects can be incredibly painful and devastating, putting all of the delight to waste.
“ There are mixed results regarding consumption of gateway drugs affecting kidney damage. Some might not affect an individual while others can cause kidney damage within a single dose. "
- Dr. Maham Zehra
What are Gateway Drugs?
A gateway drug is a “softer” drug substance, which when consumed frequently can increase dopamine levels, increasing pleasure, leading people to crave more addictive, harmful and illicit substances such as cocaine, opioids or ecstasy. Gateway substances are typically the drug most people would start with as they are served at bars, clubs and parties. A few of the most common gateway drugs consumed (especially by teens and young adults) are alcohol, nicotine and marijuana.
How do Gateway Drugs affect Kidney Function?
Chronic gateway drug consumption can deliberately lead to fluid imbalance as these substances interfere with the regulation of vasopressin, an antidiuretic hormone (ADH) assisting the kidneys by controlling the amount of urine that the body makes in regards to water retention. However, many gateway drugs, especially alcohol can restrict vasopressin release, causing the kidneys to release water into the bladder before redirecting it into the rest of the body. This displacement not only causes more urine to build up than normal, but also results in excessive fluid and electrolyte imbalances.
What is the relationship between gateway drugs and kidney stones?
Gateway drug use can damage the kidneys and increase the risk of kidney stone formation through processes like dehydration, oxidative stress and mineral imbalances. Although not all drugs can contribute to kidney stones directly, many contribute to conditions that make the formation more likely. Here is how:
The Individual
Like caffeine, the effect drug consumption has on the formation can vary depending on the individual's lifestyle, genetics and medical conditions. For example, Some individuals with conditions like heart failure or diabetes, may be more vulnerable to dehydration or mineral imbalances caused by the consumption of gateway drugs, subsequently leading to the likelihood of kidney stones.
Rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis is a life threatening condition commonly linked to substances like heroin and cocaine causing the muscles to break down. The kidneys are responsible for removing the break-up of muscle fragments (potassium, phosphate, etc.) but, if they can not get rid of these wastes quick enough, rhabdomyolysis can release excessive calcium and uric acid into the blood leading to the formation of a kidney stone.
“Basically, when a gateway drug (such as nicotine, alcohol, or marijuana) is ingested, it is absorbed through the mouth, stomach, and intestine, just like food, and is excreted via the kidneys. Any substance passing through this route can alter the blood flow to the kidneys, affecting their ability to filter waste.”
- Dr. Maham Zehra
Type of Gateway Drug Consumed
Different drugs can have different effects on the overall dynamic of the kidney and the formation of kidney stones. In a nutshell let’s look at a few:
Alcohol
While alcohol itself doesn't directly cause kidney stones, overdosing in certain alcoholic beverages can impair kidney function subsequently worsening the risk of this kidney disease. To begin, alcohol is a diuretic, causing the body to excrete more urine than normal. This can concentrate and build up levels of stone forming solutes like calcium and uric acid. Some alcoholic beverages like beer and liquor also contain exogenous purines, a molecule that breaks down into uric acid, which when consumed regularly, can build up and accumulate to form uric acid stones. Alcohol can also impair the kidneys ability to maintain the right amount of water in the body, as when there is a heavy build up of urine in the renal pelvis, the kidneys find the need to excrete as much of it as possible to maintain balance. This excursion can cause an incipient loss of urine volume leading to dehydration and concentrated minerals potentially leading to kidney stone formation. Additionally, some alcoholic beverages like wine and beer contain oxalates, which when binded with calcium can concentrate the urine (especially if the consumer is dehydrated) and contribute to calcium oxalate stones. Chronic alcohol consumption can also reduce vitamin D in the body thus reducing calcium absorption and causing calcium imbalance as alcohol can damage the liver, the organ responsible for converting vitamin D from food into 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25 (OH) D), the major form of vitamin D circulating in the bloodstream which is later converted into calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D by a process called hydroxylation. This can cause calcium imbalance because when alcohol impairs the liver, it also impairs the conversion of 25 (OH) D into calcitriol which is the hormone responsible for maintaining the regulation of calcium and phosphate in the body. When this hormone is damaged or ceases to function properly, it could lead to an increase in calcium or phosphate levels in the urine thus leading to either calcium oxalate or calcium phosphate stones.
Nicotine
Like alcohol, nicotine does not directly cause kidney stones, however, it can cause various impairments to kidney function subsequently leading to this kidney disease. For instance, nicotine is a bladder irritant meaning it can cause an overactive bladder (OAB), damaging the sensitive lining of the bladder to such an extent that it increases the frequency one may need to urinate. This happens because nicotine consumption triggers nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) in the nervous system, receptors responsible for releasing amounts of epinephrine, norepinephrine, and acetylcholine which induce detrusor muscle contractions in the bladder, emptying it via urethra even when it isn’t full. Additionally, nicotine can also cause coughing spasms, which can place pressure on the bladder causing leakage of urine. It can also weaken pelvic floor muscles, making bladder control more difficult, supporting this factor. Nicotine can also be a major cause of oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is when there is an increase of highly reactive molecules called free radicals or reactive oxygen species (ROS) (molecules that can cause chronic diseases and tissue damage) and there are not enough antioxidants to suppress them. This can be a subsequent cause of kidney stone formation as oxidative stress can cause damage and eject stone-forming minerals into your system. Nicotine is also a large factor in regards to ejection of stone-forming minerals as like alcohol, nicotine is a diuretic. And lastly, nicotine has been shown to hamper bone development and density making its effects associated with the Parathyroid hormone (PTH). The Parathyroid hormone is a hormone produced by the parathyroid glands that is released in response to low calcium levels in the blood. It is released by stimulating osteoclasts to break down the bones to collect calcium and phosphate from them into the bloodstream to then have calcium reabsorbed by the kidneys, back into the bloodstream instead of letting it get lost in the urine, and have the phosphate excreted into the urine instead. However, short-term nicotine exposure can disrupt the calcium-sensing receptors (CaSR) in the parathyroid glands making them less responsive to low calcium levels, decreasing PTH release. What this does is when the blood is in need of calcium, instead of signaling the kidneys to reabsorb the calcium back into the bloodstream, it allows the calcium to be excreted into the urine. This does not only decrease calcium levels in the blood (hypocalcemia), but can also lead to excessive calcium excursion in the urine (hypercalciuria), allowing minerals like oxalates or phosphates to bind with it and eventually nucleate forming kidney stones. This is a condition known as hypoparathyroidism. Furthermore, long-term nicotine exposure can cause secondary hyperparathyroidism, a rare condition in which abnormal amounts of PTH is released by the parathyroid hormones by an external factor (in our case nicotine) leading to excessive amounts of calcium in the urine (hypercalciuria). This happens because over consuming nicotine can decrease vitamin D levels, making calcium absorption in the intestines and blood notably low (hypocalcemia). At this stage, excessive PTH will be released leading to osteoporosis (excessive bone breakdown caused by osteoclasts collecting to much calcium and phosphate from them) and hypercalciuria (excessive calcium excursion in urine), because when the PTH glands produce to much calcium and phosphate, the kidneys may not be able to reabsorb all of it back into the bloodstream leading to excessive amounts of it in the urine, further aiding in calcium phosphate or oxalate kidney stone formation if binded together.
“ Caffeine: People with kidney stones are often advised to increase their fluid intake to help pass the stones and prevent new ones from forming. If someone consumes a lot of caffeine, it may undermine this advice.
Gateway Drugs: Certain substances, like nicotine, may worsen oxidative stress, while others (e.g., alcohol) may influence calcium or uric acid levels, complicating treatment aimed at preventing future stones. “
- Dr. Maham Zehra
What are Gateway Drugs?
Illicit drugs are ”harder” drugs, typically consumed after finding pleasure in gateway drugs and craving to have something more powerful. The effects of using such drugs include: chronic diseases (liver, kidneys, etc.), blood borne viruses and even mental health problems and increased suicide risks. Illicit drugs are the same thing as illegal drugs meaning they are drugs which were not prescribed by a professional and instead were bought at a drugstore. Examples of illicit drugs include heroin, Hallucinogens and even cocaine and MDMA/Ecstasy, which we will be looking at now:
Cocaine
Frequent consumption of cocaine can cause the blood vessels to narrow just enough to block the passageway of blood flow to the kidneys (vasoconstriction). This can be a subsequent cause of oxidative stress (imbalance of antioxidants in the body) and changing the balance of minerals calcium, inducing kidney stone risk.
Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) / Ecstasy
Ecstasy, the street name for Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), is a widely abused drug declining the kidneys ability to function by a syndrome known as hyponatremia (decrease in sodium levels in blood [135-145 milliequivalents per liter]) that can be mild to life threatening. MDMA can also potentially lead to stone formation by hyperthermia (body temperature is higher than normal [98.6 °F / 37 °C]), a common syndrome caused by MDMA, concentrating minerals in the urine. Dehydration also plays a role as it is affected significantly by MDMA.
Hydration Levels
Various drugs including cocaine and MDMA contribute to the clause of overheating and dehydration by impairing the kidneys ability to regulate fluids. Dehydration is a direct cause of concentrated urine, which allows the urine minerals to get saturated and nucleate.
“ While I have never consumed any gateway or illicit substances, I was addicted to sugary sodas, tea, ice caps and other delights rich in oxalates. When my doctor informed me that my stone composition (calcium oxalate) had been formed by these drinks, I vowed to limit this consumption as much as possible. Now, 3 years later, I have opted for more natural alternatives like fresh juices. I also make sure I am always hydrated by keeping a water bottle by my side at all times. Lastly, I have limited sweets for special occasions only.”
- Akbar Rais
Background Research
This research is not linked to caffeine or addictive substances. However, it was written to help educate us on why kidney stone prevention is so important by researching the symptoms, potential infections/diseases involved, surgeries and many more.
How do Kidney Stones affect Kidney Function?
Interesting enough, kidney stones do not affect kidney function the moment that they are formed. Rather they cause significant changes when they detach themselves from the kidney tissue or the renal pelvis and enter the ureter, the tubes that connect the kidneys and the bladder. The walls of the ureters are lined with smooth muscles that contract to push urine by peristalsis. These contractions also help push the stone along, but because the ureters are very narrow, the stone can cause stretching, swelling, involuntary ureter contractions (spasm) and even cause one to tremble from pain in their sides and back in their lower abdomen. At this stage, 3 things may happen:
1. Blockage of Urine Flow (Ureteral Obstruction)
Most kidney stones are small (less than 5 mm) and pass on their own without causing any symptoms, pain and little to no harm to the ureter or urinary tract. However, some kidney stones are larger in scale (more than 5 mm) and can get lodged in the ureters, blocking urine flow (ureteral obstruction). Ureteral obstruction also prevents urine from entering the bladder and exiting the body via urethra. If this obstruction is not treated and removed, one may develop a condition called hydronephrosis.
Hydronephrosis
Hydronephrosis is the buildup of urine in one of or both of the kidney(s) in the renal pelvis. This buildup is usually caused by a blockage in the urinary tract blocking the passageway for urine to exit the body through the urethra and instead, flow the back up into the kidney causing the kidney to swell and stretch and even develop a condition called necrosis (death of body tissue). This can cause one to feel excruciating side and back pain, fever, vomiting and painful urination. Sometimes, professionals may grade the level of hydronephrosis on a scale of 1 to 4, 1 representing minimal dilation and 4 representing extreme dilation. But, what factors of ureteral obstruction affect the severity of dilation? In a nutshell, here are a few:
- Degree of obstruction
- Duration of Obstruction
- Stone Compounds and size
- Kidney Function
- Presence of infection
- Time of detection
2. Infection
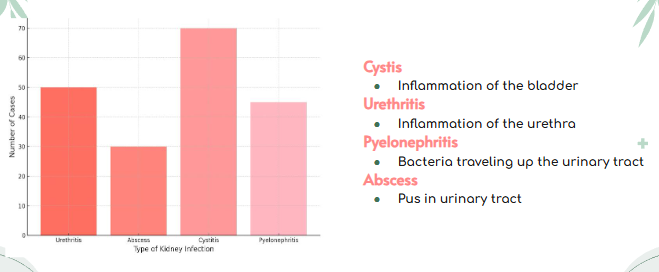
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is a common infection caused by bacteria that enter your body through the urethra and multiply, infecting the urinary tract. UTI’s need significant medical treatment. If treated poorly or after a long period of time, the bacteria can spread into the bloodstream (septicaemia) causing long lasting kidney damage and severe infections such as urethritis, abscess, cystitis or pyelonephritis, a serious infection that resides in the kidneys most commonly by kidney stones themself. UTI can also cause septic shock, further damaging the kidneys.
3. Kidney Failure
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI), also known as Acute Renal Failure (ARF) is a disorder where the kidney is suddenly unable to function. This is a severe condition that can develop within a few hours or days. Most people can develop AKI within 48 hours but for others it can take as long as 7 days. Kidney stones can cause AKI in the following ways:
Bilateral Obstruction (BUO)
Bilateral Ureteral Obstruction (BUO) is the blockage in both ureters and can cause such a severe dilation to the renal pelvis (kidney gland that collects urine) that it blocks kidney function entirely (hydronephrosis). However, the development of AKI depends on how quickly the obstruction is treated. If the ureters are obstructed for a long period of time, it can increase pressure in the kidneys, damage kidney tissues and reduce blood flow leading to moderate to severe levels of AKI. On the other hand, if the obstruction is treated and removed early on, it can prevent AKI even in cases of severe dilation
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD), also known as chronic kidney failure, is a term used to describe a repetitive and irreversible loss of kidney function over time. Advanced CKD can even cause dangerous levels of waste, fluid and electrolytes to build up in your body. Chronic episodes of kidney stones can trigger CKD through recurrent obstructions, fibrosis (tissue scarring), and loss of nephrons (blood filters in kidney).
End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
End stage renal disease (ESRD), also called end stage renal failure, is the last and permanent stage of CKD, where the kidney function has declined so severely that it has reached the point where it is not able to function on its own. However, the odds of kidney stones being a direct cause of ESRD is relatively low, but there are still some possible factors that can influence the risk of ESRD directly from kidney stones such as:
- Struvite and cystine stones
- Recurrent kidney stones
- Delayed diagnosis / Poor treatment
- Infections
- Acute kidney injury (AKI)
A patient with ESRD must receive dialysis (a treatment that filters and removes extra fluid from the body) or a kidney transplantation in order to survive for more than a few days.
How are Kidney Stones Diagnosed?
Kidney stones can cause excruciating pain to an individual leading them to seek immediate medical attention. At this stage after taking note of your condition, symptoms, family history and risk factors, a professional may proceed to take these diagnostic procedures:
Urinalysis Tests
Urine tests, also known as urinalysis, is a 24 hour urine collection test showcasing whether or not your body is producing high concentrations of uric acid, or any other minerals contributing to the development of kidney stones. It can also detect many disorders including, UTI’s, diabetes and kidney disease. Urinalysis can cause a common kidney stone symptom called hematuria, or blood in urine.
Hematuria
Hematuria is the medical term for the presence of red blood cells in urine. While it is a common indicator of kidney stones, it can also be a symptom of UTI or other kidney diseases. In the case of kidney stones, hematuria often occurs when the stone moves or remains anchored in the narrow space of the ureter, the sharp edges of the stone begin scraping its frail, delicate lining causing minor bleeding. Hematuria can be of 2 types, gross and microscopic, gross hematuria is when there is enough blood present in the urine that you can see with your naked eye. On the other hand, microscopic hematuria is when your urine does have small amounts of blood in it but is not visible with other than a microscope.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are another way professionals may diagnose kidney stones. While these tests cannot determine whether or not you have a stone, it can monitor high levels of calcium and uric acid in the blood, which can contribute to the final diagnosis of kidney stones. Blood tests can also monitor how healthy your kidneys are, allowing your doctor to check you for any other medical conditions.
Imagine Tests
After diagnosing a patient for kidney stones, a professional usually uses imaging tests to locate where the stone is in the urinary tract. The types of imagine tests used for diagnosing kidney stones include:
Abdominal X-Ray
While it is not frequently used on an average patient, abdominal X-Rays can be a great way a professional can view the placement of larger kidney stones on a patient with other medical conditions like pregnancy, as these scans use low levels of radiation making it safer for a pregnant woman and her baby. However, abdominal X-Rays can sometimes miss smaller stones reducing its accuracy when dealing with an average patient.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan
Unlike X-Rays, CT scans provide accuracy revealing even the tiniest of stones. They can also provide a clear picture of where the stone is located, whether or not it is creating ureteral obstruction, and even the conditions that may have caused the stone to form.
Ultrasound
An ultrasound is another tool used on a patient to detect the placement of kidney stones. While there is not too much information on this diagnostic exam in relation to kidney stones, it can be inferred that it is relatively safe as it produces low levels of radiation making it suitable for patients with external medical conditions.
Analysis of Passed Stones
A kidney stone analysis is a lab test to see what chemicals the kidney stone is made up of (calcium, uric acid, etc.) the test is done on a kidney stone either passed through the urethra (a professional may ask you to urinate through a strainer or a stent to catch the stone) or on a kidney stone that was removed during surgery. They may also prescribe you with a medication known as floxate, a drug used to reduce muscle retention. A chemical analysis of a kidney stone can not only guide treatment but can also provide your doctor with enough information to determine what caused your kidney stone(s) and what protective measures you can take to avoid kidney stones in the future.
“ Caffeine: Caffeine-induced dehydration could alter urine concentration, which might make it more difficult for doctors to assess hydration status accurately.
Gateway Drugs: Certain drugs like diuretics can increase calcium in the urine, while others can affect uric acid or oxalate levels, making it harder to pinpoint the stone's exact cause. “
- Dr. Maham Zehra
“My healthcare provider diagnosed both of my kidney stones by urine tests and an ultrasound. The urine tests revealed that I had microscopic hematuria and the ultrasound led doctors to conclude my case as it showed where my kidney stones resided.”
- Akbar Rais
What Procedures Are Used to Remove Kidney Stones?
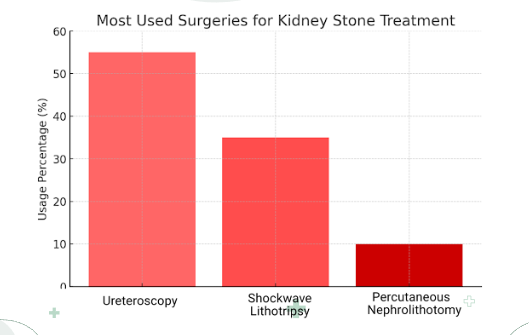
While most kidney stones can pass on their own, sometimes a stone can be so large that it gets lodged into the ureters having no way to exit your body, at this stage it is called obstructive ureterolithiasis. When this happens your doctor may consider surgery as the most profound treatment. The types of kidney stone surgeries include :
Ureteroscopy (URS)
Ureteroscopy (URS) is the most common procedure used to treat kidney stones. It involves the passageway via urethra, of a long, thin tube called a ureteroscope, consisting of an eyepiece on one end and a small lens and light on the other, similar to a telescope. This device is used to locate the stone in the ureter as well as determine its size and composition so that your healthcare provider can identify the best ureteroscopy surgery for you. Ureteroscopy surgeries are of 2 types:
1. Basket Extraction
A Basket Extraction is a ureteroscopy procedure used for extracting small kidney stones. This extraction tool is an extended version of a ureteroscope in which an extra channel holds a wire basket, A device that can collect the stone whole and guide it down to the bladder before passing it out through the urethral opening.
“My healthcare provider removed both of my kidney stones using Ureteroscopy with basket extraction. I felt absolutely no pain or had any chronic or acute symptoms or complications during or after the procedure. My doctor also provided me with antibiotics, helping me get back to my usual lifestyle instantly.”
- Akbar Rais
2. Laser Lithotripsy
In cases of a large kidney stone, a healthcare professional may suggest a laser lithotripsy ureteroscopy. In this procedure, a flexible fiber with a laser beam illuminating through the lens, with rays strong enough to break apart the stone into small fragments. These fragments are then individually extracted from the body using a wire basket. Both Ureteroscopy techniques require no incision and little to no pain as a patient is put into anesthesia. Furthermore, a ureteroscopic surgery takes no longer than 1 to 3 hours for the average patient making it an outpatient procedure (letting you go home the same day). However, there are significant risk factors going through with this procedure such as UTI’s and injuries to the ureter, though this can easily be prevented as a professional will prescribe you with antibiotics after the surgery to reduce the risk.
Shockwave Lithotripsy (SWL)
Shockwave lithotripsy (SWL) also called Extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy (ESWL), is a procedure used for stones softer and less than 2 centimeters in size. In this procedure, a professional uses an X-Ray to locate the stone and soundwaves to break it up. These soundwaves (several hundred to thousands) are transmitted out of a device called a lithotripter. These broken fragments are then passed naturally with the urine. Like Ureteroscopy, ESWL is an outpatient procedure, spanning over 30 minutes to an hour, depending on the stone size, hardness and location. It is also a considerably safe procedure with high success rates, no pain as a patient is put under anesthesia, natural stone passing, and for most patients, short recovery time, allowing you to return to your normal lifestyle within a few days. However, some patients may experience hematuria or slight discomfort in their body though can easily be prevented by increasing your water intake to help stone fragments pass and by asking your doctor for oral pain medications such as aspirins to reduce discomfort.
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) is a major surgery when it comes to kidney stones. It is done when other surgeries are unsuccessful or on larger stones. In this procedure, a professional will make a small incision in your back or side and then remove the kidney stone with a instrument called a nephroscope to locate the stone and then use ultrasonic or laser energy to break the stone into smaller fragments and then remove it or use other tools attached to the nephroscope to remove it entirely. PCNL is a highly effective surgery with high success rates and like other kidney surgeries, a patient experiences no pain as they are under anesthesia. However, unlike the other procedures after a PCNL takes place, a patient would need to stay about a day or two in the hospital before going home. The aftermath of the procedure is also usually moderately painful to most patients though a healthcare provider can prescribe you with painkillers to reduce the pain.
Who is most likely to develop Kidney Stones?
Demographic Factors:
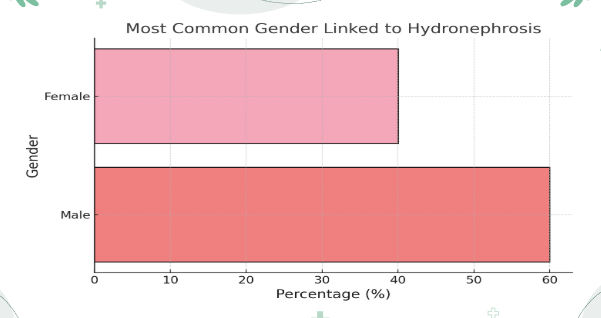
- Gender: Men
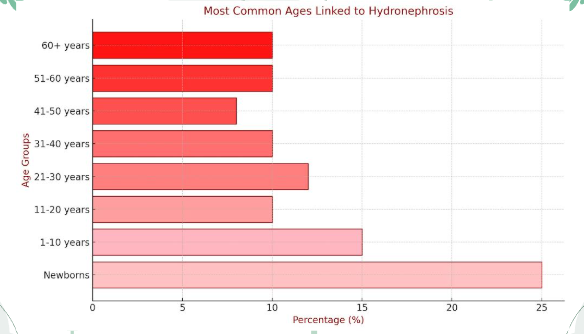
- Age: 30-60
- Ethnicity: Non-hispanic white individuals
Medical History:
Family History: Having a family member who has had kidney stones in the past increases your risk of developing kidney stones significantly.
Personal History: Having a kidney stone in the past increases the chance of developing one again (recurrent nephrolithiasis)
Environmental Factors:
- Individuals living in hot climates are more prone to kidney stones due to dehydration.
Medical Conditions:
- Diabetes
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
- Renal tubular acidosis
- Cystinuria
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Many More!
What symptoms do Kidney Stones Cause?
- Collicky pain on the sides/back
- Constant stomach ache
- Foul smelling ; cloudy urine
- Blood in urine (hematuria)
- Fever
- Nausea
- Chills
- Vomiting
“Both of my kidney stones remained lodged in my ureters for about 2 weeks causing me excruciating pain. I felt sharp, colicky pain in the left side of my bladder causing me to shiver in agony when an ambulance had driven me to the hospital. By far, the most painful experience of my life.”
- Akbar Rais
What medications are used to treat Kidney Stones?
- Alpha Blocker
- Thiazide Diuretics
- Allopurinol
- Potassium Citrate
Data
Figure 1: Types of Kidney Stones
Figure 2: Types of Kidney Diseases
Figure 3: The effects of caffeine on the body
Figure 4: The effect of urine acidity or alkalinity on kidney stone formation
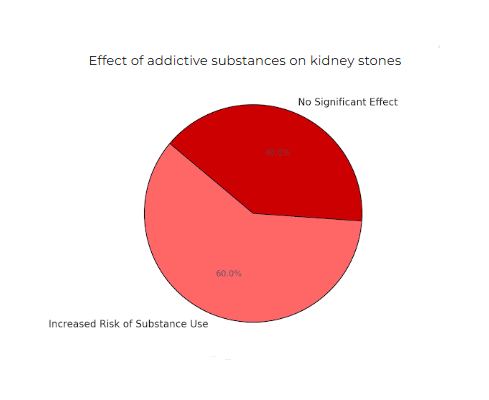
Figure 5: The effect of addictive substances on kidney stones
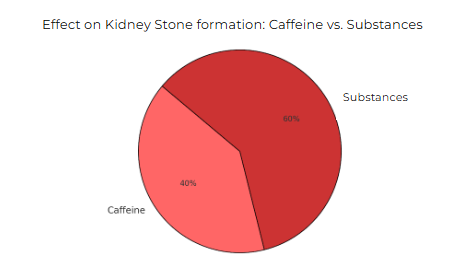
Figure 5: The greater risk factor for kidney stones: caffeine vs. substances
Figure 6: The most common gender linked to hydronephrosis
Figure 7: The most common age linked to hydronephrosis
Figure 8: The different types of Urinary Tract Infections (UTI)
Figure 9: The most used surgeries surgeries for kidney stone treatment
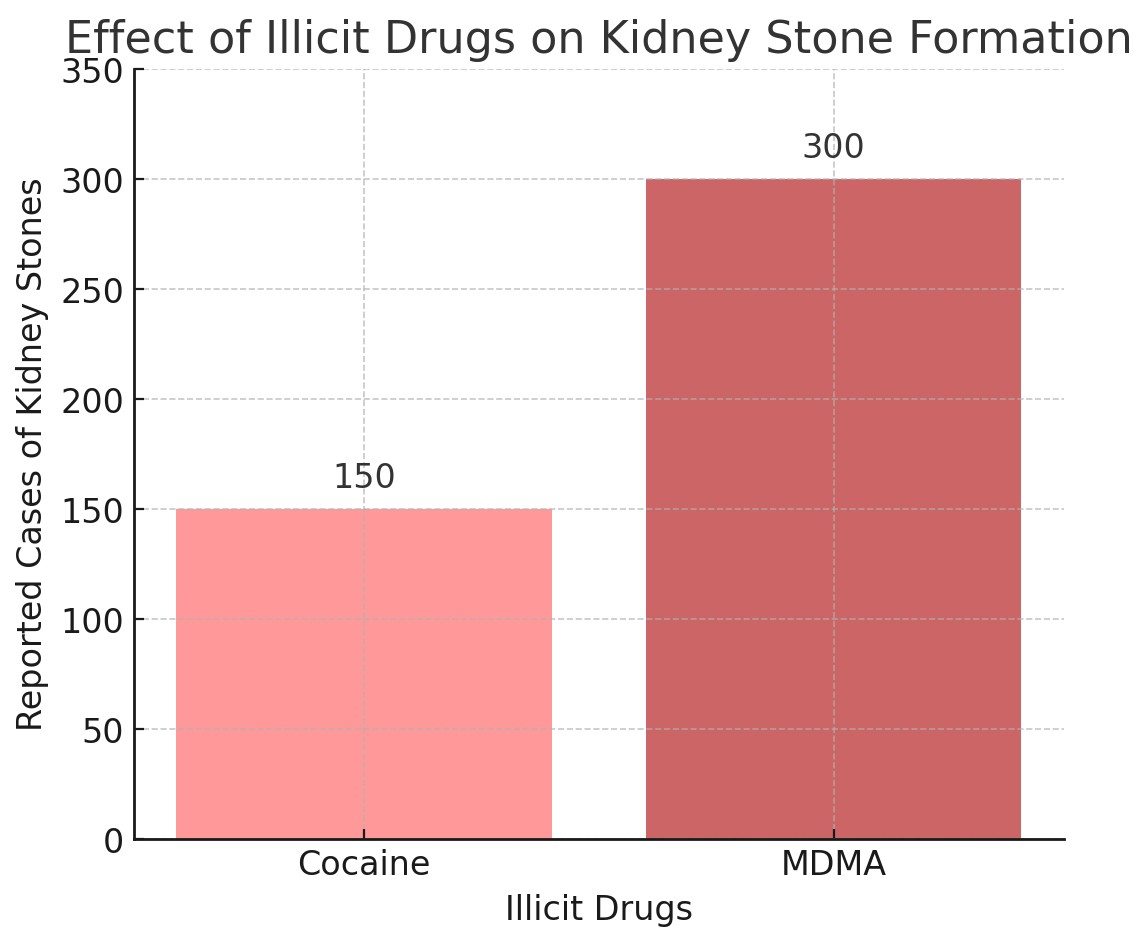
Figure 10: The most effective illict drug on kidney stone formation
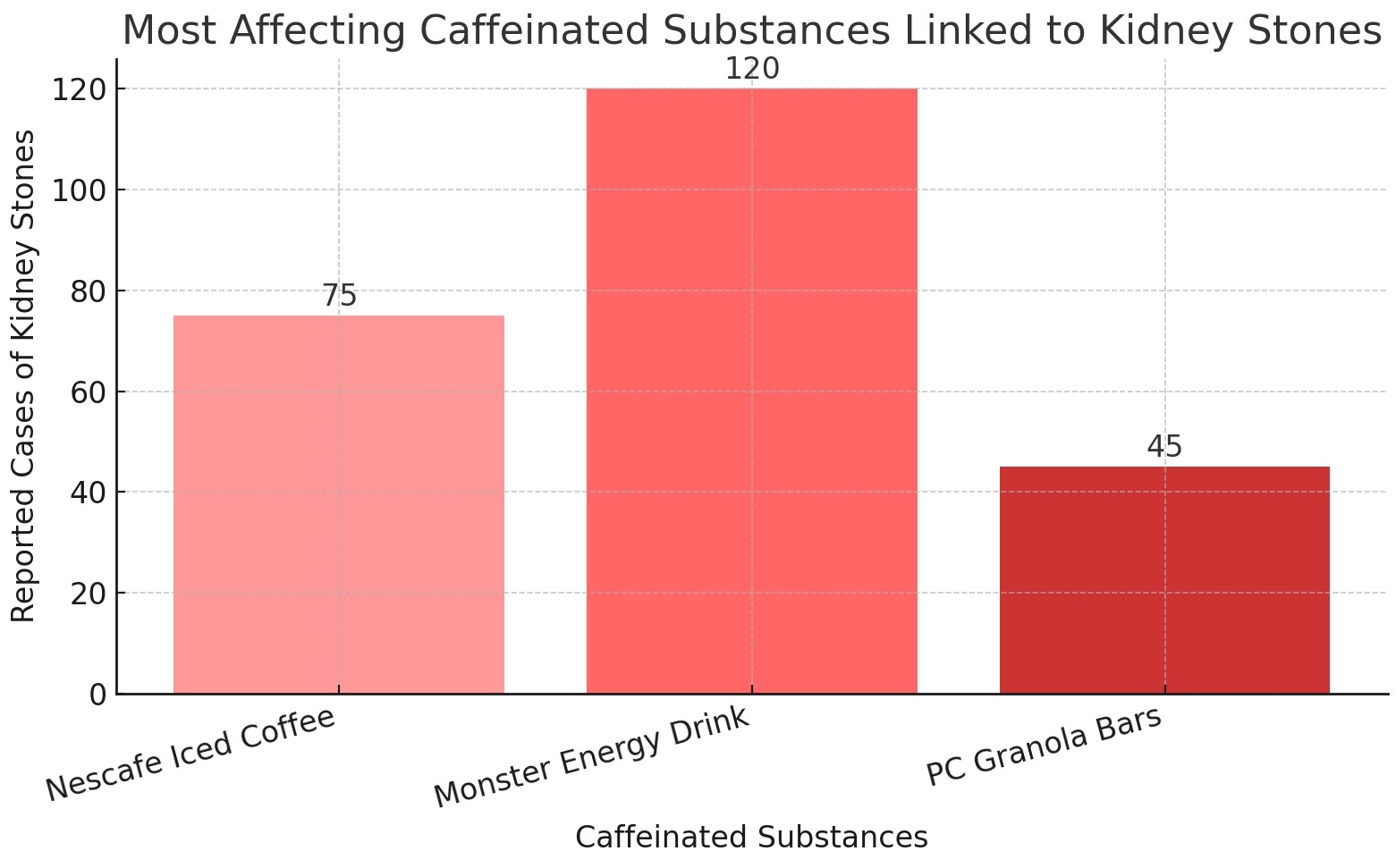
Figure 11: The most effective caffeinated substance on kidney stone formation
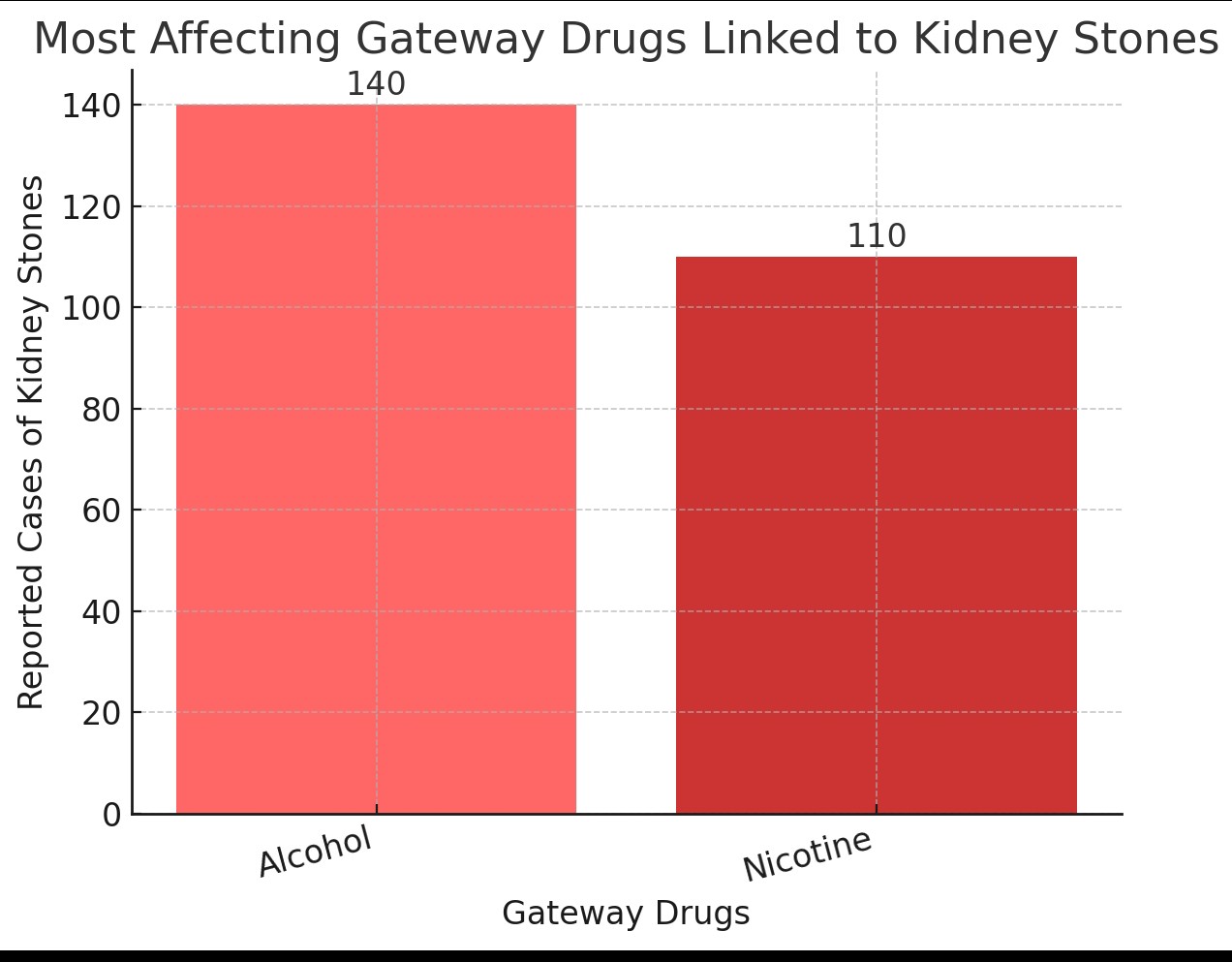
Figure 12: The most effective gateway drug on kidney stone formation
Figure 13: Displays the process of calcium clearence
Conclusion
In conclusion, my hypothesis was mostly correct. Caffeine and addictive substances have an effect on kidney stone formation through processes like oxidative stress and mineral imbalances, but also dehydration, which teaches us the importance of staying hydrated as this is one of the most important factors contributing to kidney stones.
In regards to my hypothetical guesses on which substances had a greater impact on kidney stone formation, my results were:
- Caffeine: I was correct, Monster Energy drinks pose a greater risk as it acts as a diuretic and is highly acidic, increases calcium excursion and promotes insulin resistance. Nescafe Iced Coffee can also fall as a close second if heavily sweetened. While President's Choice granola bars do not contain many oxalates, excess acid or caffeine making them unlikely to contribute to kidney stone formation.
- Illicit Drugs: I was incorrect, I hypothesized that cocaine is of greater effect but it is actually MDMA. This is because MDMA poses for more long term and serious effects as MDMA can cause severe overheating and therefore chronic dehydration. Cocaine can also cause many similar effects, however cocaine poses to cause kidney damage rather than cause kidney stones.
- Gateway Drugs: I was correct, Alcohol poses a greater risk of kidney stones in comparison to nicotine as many alcoholic beverages contain heavy concentrations of oxalates and have many other effects in relation to calcium excursion and dehydration. While nicotine also has similar qualities, long term exposure is what would cause them, whereas alcohol can in a shorter period of time.
And finally, my hypothesis on the greatest substance acting on kidney stone formation was also correct. It is true that addictive substances have a greater impact on kidney stones than caffeine due to their more severe effects on kidney dysfunction leading to this kidney disease. This is also because caffeine contributes to about 5% of urine concentration as the other 95%’s diuretic effect is notably low. As for addictive substances, they have more indirect yet serious impacts on kidney stones affecting around 5-10% of kidney stone cases. However, this is a rough estimate as studies linking addictive substances to kidney stones are very limited. For a more accurate estimation, this topic may require further study.
It is also true that illicit drugs have a greater impact on kidney stone formation due to the fact that illicit drugs are much stronger and can cause many health defects and medical conditions.
Advice from Dr. Maham Zehra & Akbar Rais
“ I was a teenager preparing for MCAT when I had a kidney stone. I was so stressed and focused on studies that I did not take care of my health. I skipped meals, stayed up all night on caffeine and drank less fluids which ended up causing severe backache and a 0.5cm kidney stone. I remember that I had to be on painkillers and the scan showed swelling in my urinary tract. The doctor advised me to drink at least 4 liters of water a day. Luckily, the stone excreted itself and I did not need any treatment. That’s when I learned the importance of staying hydrated as it dilutes the effect of caffeine and addictive drugs. “
- Dr. Maham Zehra
“ I was completely unaware of my amount of caffeine intake until this experience had struck me. I highly recommended everybody, especially teens to set limitations to your intake of sugar and to always stay hydrated. This was by far one of the toughest experiences of my life and I would hate for anyone to go through anything like it. Always remember that there are countless safer options that can satisfy your needs just as much as sugar/caffeine do. As for addictive drugs, while I have not consumed any myself, it is important to know that it can cause serious damage to vital organs in your body potentially costing you your life. “
- Akbar Rais
Citations
Used For: What are Kidney Stones?
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15604-kidney-stones
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/kidney-stones
Used For: How do Kidney Stones affect Kidney Function?
https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/kidney-stones
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/kidney-stones/symptoms-causes/syc-20355755
https://humanbiology.pressbooks.tru.ca/chapter/18-5-ureters-urinary-bladder-and-urethra/#:~:text=16.5%20Summary-,Ureters%20are%20tube%2Dlike%20structures%20that%20connect%20the%20kidneys%20with,through%20the%20ureter%20by%20peristalsis.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ureteral-obstruction/symptoms-causes/syc-20354676
https://www.michaelrotmanurology.com/blog/follow-these-top-warning-signs-indicating-you-may-have-kidney-stones
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21155-ureteral-obstruction
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/kidney-stones
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hydronephrosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20575276https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/hydronephrosis/causes/#:~:text=Some%20of%20the%20main%20causes,swelling%20of%20the%20prostate%20gland
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK563217/#:~:text=Hydronephrosis%20is%20defined%20as%20dilatation,urine%20outflow%20is%20called%20hydroureter.
https://www.med.unc.edu/urology/pediatrics/pediatric-conditions/hydronephrosis/#:~:text=Sometimes%20hydronephrosis%20is%20given%20a,or%20both%20kidneys%20(bilateral).
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9123473/#:~:text=By%20definition%2C%20upper%20urinary%20tract,%2C%20trauma%2C%20strictures%20and%20tumors.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3235203/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/books/NBK560674/
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15417-hydronephrosis
https://www.kidney.org/top-5-jobs-kidneys-do
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/kidney-infection/symptoms-causes/syc-20353387
https://www.cdc.gov/uti/about/index.html#:~:text=UTIs%20are%20common%20infections%20that,up%20the%20urethra%20a…
https://www.kidney.org/kidney-topics/urinary-tract-infections#:~:text=People%20with%20blockages%20in%20their,urine%20and%20cause%20a%20UTI.
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/urinary-tract-infections
http://www.urologyhealth.org/urology-a-z/k/kidney-infection-(pyelonephritis)
https://www.kidney.org/kidney-topics/acute-kidney-injury-aki#:~:text=Acute%20kidney%20injury%20(AKI)%20occurs,the%20term%20'acute%20renal%20failure.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5198510/
https://www.yalemedicine.org/conditions/acute-kidney-injury
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/end-stage-renal-failure#:~:text=End%2Dstage%20renal%20failure%2C%20also,longer%20function%20on%20their%20own.
https://kidney.ca/Kidney-Health/Living-With-Kidney-Failure/Dialysis
Used For: How are kidney stones diagnosed?
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/kidney-stones/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20355759
https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/urinalysis/about/pac-20384907
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15234-hematuria
https://www.beaumont.org/treatments/kidney-ureteral-stones-diagnosis#:~:text=Blood%20tests%20%2D%20Blood%20tests%20cannot,how%20healthy%20your%20kidneys%20are.
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/kidney-stones/diagnosis
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/ct-scan-of-the-kidney#:~:text=CT%20scans%20of%20the%20kidneys%20are%20useful%20in%20the%20examination,and%20the%20location%20of%20abscesses.
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/kidney-ultrasound
https://myhealth.alberta.ca/Health/pages/conditions.aspx?hwid=hw7826#:~:text=Test%20Overview,-Kidney%20stone%20analysis&text=The%20test%20is%20done%20on,prevent%20more%20stones%20from%20forming.
Used For: What Procedures Are Used to Remove Kidney Stones?
https://nyulangone.org/conditions/kidney-stones/treatments/surgery-for-kidney-stones#:~:text=Percutaneous%20Nephrolithotomy,-Percutaneous%20nephrolithotomy%20is&text=In%20this%20procedure%2C%20a%20surgeon,order%20to%20completely%20remove%20them.
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/ureteroscopy
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/16213-ureteroscopy
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/procedures/16285-holmium-laser-lithotripsy
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/kidney-stones/extracorporeal-shock-wave-lithotripsy-eswl
https://www.kidney.org/kidney-topics/extracorporeal-shock-wave-lithotripsy-eswl#:~:text=Here's%20how%20each%20one%20works,break%20them%20into%20smaller%20pieces.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/17349-percutaneous-nephrolithotomy
Used For: What is the relationship between caffeine and kidney stones?
https://www.kidney.org/press-room/new-study-supports-coffee-and-caffeine-can-reduce-kidney-stones-risk
https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/expert-answers/caffeinated-drinks/faq-20057965#:~:text=As%20a%20chemical%2C%20caffeine%20increases,of%20urine%20the%20body%20makes.
https://www.cincinnatichildrens.org/health/h/hypercalciuria#:~:text=What%20is%20Hypercalciuria%3F,with%20normal%20blood%20calcium%20levels.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hyperoxaluria/symptoms-causes/syc-20352254#:~:text=The%20body%20gets%20rid%20of,hyperoxaluria%2C%20kidney%20stones%20form%20early.
https://health.clevelandclinic.org/coffee-dehydration
https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/healthyliving/caffeine#where-to-get-help
https://www.vogue.com/article/unhealthy-foods?utm_
https://athleticmindedtraveler.com/blog/energy-bars-and-protein-shakes-can-cause-kidney-stones
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0085253815529517#:~:text=Fructose%20intake%20may%20also%20increase,the%20production%20of%20uric%20acid.
Used For: What is substance abuse?
https://www.health.gov.au/topics/drugs/about-drugs/what-are-drugs
https://americanaddictioncenters.org/health-complications-addiction/renal-system
https://americanaddictioncenters.org/health-complications-addiction/renal-system
https://health.howstuffworks.com/wellness/drugs-alcohol/hangover2.htm
https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.cancer.gov%2Fpublications%2Fdictionaries%2Fcancer-terms%2Fdef%2Fvasopressin&psig=AOvVaw068NHnO5i0r-GLY0a8Esb4&ust=1740982164221000&source=images&cd=vfe&opi=89978449&ved=0CAYQrpoMahcKEwjw36qY3uqLAxUAAAAAHQAAAAAQBA
https://www.kidney.org/kidney-topics/alcohol-and-your-kidneys
https://creakyjoints.org/about-arthritis/gout/gout-diet/alcohol-and-gout/
https://www.arthritis-health.com/types/gout/what-are-purines
https://www.healthline.com/health/osteoporosis/osteoporosis-and-alcohol#causation
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3296927/
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2088694-overview?form=fpf
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8708000/ https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33852164/#:~:text=Caffeine%20increased%20renal%20calcium%20clearance,in%20the%20proximal%20convoluted%20tubule.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3940208/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21170875/#:~:text=The%20formation%20of%20various%20types,uric%20acid%20or%20cystine%20stones.
https://healthwire.pk/healthcare/kidney-stones-from-energy-drinks/#oxalates
https://www.thekidneydietitian.org/do-energy-drinks-cause-kidney-stones/
https://www.mountsinai.org/care/urology/services/kidney-stones/prevention#:~:text=Sodium%20causes%20the%20kidneys%20to,formation%20of%20calcium%20oxalate%20stones.
https://www.onlymyhealth.com/how-artificially-sweetened-drinks-can-increase-the-risk-of-kidney-stones-1707982873
https://www.kidney.org/news-stories/coffee-and-kidney-disease-it-safe#:~:text=In%20summary%2C%20coffee%20is%20an,and%20phosphorus%20content%20of%20coffee.
https://www.kidney.org/kidney-topics/kidney-stones#:~:text=Most%20kidney%20stones%20are%20formed,also%20has%20too%20much%20salt.
https://nyulangone.org/conditions/kidney-stones/treatments/medications-dietary-changes-for-kidney-stones#:~:text=Your%20doctor%20may%20prescribe%20potassium,prevent%20uric%20acid%20kidney%20stones.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/drugs/20766-potassium-chloride-extended-release-capsules-or-tablets
https://www.centraltexasurology.com/does-smoking-make-you-pee-a-lot/
https://www.news-medical.net/health/Nicotine-and-Oxidative-Stress.aspx#:~:text=Nicotine%20also%20triggers%20an%20increase,%2C%20and%20peroxide%20(H2O2).
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-66937-7#:~:text=Our%20research%20indicates%20that%20tobacco,to%20parathyroid%20dysfunction%20in%20adults.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hyperparathyroidism/symptoms-causes/syc-20356194
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hypoparathyroidism/symptoms-causes/syc-20355375
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2669834/
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/osteoporosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20351968
Used For: What is the relationship between gateway drugs and kidney stones?
https://americanaddictioncenters.org/health-complications-addiction/renal-system
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21184-rhabdomyolysis
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/oxidative-stress
https://wjnu.org/index.php/wjnu/article/view/428/371#:~:text=Patients%20with%20kidney%20stones%20may,opioid%20exposure%20for%20these%20patients.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15427-urinary-retention
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/3_4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22111-hyperthermia
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hyponatremia/symptoms-causes/syc-20373711#:~:text=A%20normal%20blood%20sodium%20level,Certain%20medications.
https://sdf.org.uk/staying-hydrated-when-using-substances/
Used For: Who is most likely to develop kidney stones?
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9869853/
Used For: What symptoms do kidney stones cause?
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/kidney-stones/symptoms-causes/syc-20355755
https://www.kidney.org/kidney-topics/kidney-stones
Used For: What medications are used to treat kidney stones?
https://nyulangone.org/conditions/kidney-stones/treatments/medications-dietary-changes-for-kidney-stones
Acknowledgement
I would like to thank :
-
Dr. Maham Zehra for sharing her expertise on kidney health with me
-
Akbar Rais (my father) for taking the time to share his experiences with me and helping me make a kidney model for the CYSF
-
My science teacher, Mrs. Nambiar for her guidance
-
My substitute teacher, Ms. Harvey, for discussing her experiences with me
-
My family for supporting me throughout this project.