Affect of Chemicals in Water Given to Radishes on its Growth and Edibility
Grade 7
Presentation
No video provided
Hypothesis
Introduction
In this project, I will explore the effect of different chemicals, specifically hydrocarbons, sodium chloride, and coconut milk on the radish plant. The radish plant is one of the healthiest root vegetables in the world. There are about seven million metric tons of radish worldwide right now, mostly produced in East Asia, particularly by China, Japan, and South Korea. This experiment will be helpful to farmers when they identify the chemicals in their particular quadrat or arable land, and if they need to move their crops or not.
Bases
Humans and plants are similar in many ways, they share many of the same biochemical compounds, which are carbon-based compounds that make up cells in living things. They also use similar processes and they both need water. For us, pure water with less harmful bacteria is better, although 100 % pure water can kill you, this is mostly true.
Hypothesis
Based on the information I already knew about this topic stated above, I hypothesize that the control, the subject that I didn't tamper with its water would grow best. A point that may later prove my hypothesis wrong is that if the manipulated variable doesn't act as expected and becomes a substance similar to chemical fertilizers.
Research
Basic Needs of the Radish
The basic needs of all plants are food/ nutrients, water, sunlight, and temperature. I will assess the radish based on these and some other parameters.
Food/ Nutrients
Radishes need moderate potassium, meaning they don't want too much but cannot get by on too little. This vegetable needs moderate phosphorous and little nitrogen. The ideal fertilizer for radishes would be monopotassium phosphate fertilizer as it meets this plant's needs. The amount of nutrients this plant needs makes it a straightforward plant to care for.
Space and Water
Each radish bulb needs about 4 - 8 inches of space. This is based on the soil and the amount of potassium and phosphorous in the soil per square inch. The radish needs plenty of water about half a cup a day. The most important matter is to keep the soil moist. If the soil is not moist this will cause the roots to develop a bad taste. Excess amounts of water will cause the root to spoil and rot.
Light and Temperature
The radish needs full sun meaning about six hours of direct sun a day. This is necessary as growing the plant in the shade will cause it to focus on developing its leaves rather than its roots, which is the part that humans use the most. This plant is more resilient towards cold weather, its optimal temperature range being from 10 degrees Celsius to 21 degrees. Higher temperatures will cause the root to become woody or spongy and have a hollow center. The spongy center is the result of the cell walls of the plant separating due to the hot weather.
Soil
Radishes grow best in loam or a little bit of sandy soil that has good drainage its roots can grow easily. The soil in which the radish grows must not be very packed together as then the roots will have difficulty growing into the most they can be.
Effects of Hydrocarbon on General Plants
Hydrocarbons are an organic chemical compound that is the basis of many important energy sources. This chemical compound can interfere with plant growth in a few scenarios:
- Pipeline accidents in fields
- Unauthorized collection of petroleum through oil pipelines
- Leaks in fields due to unauthorized collection of petroleum through oil pipelines
These are some of the effects of Hydrocarbons on plants:
- Hinder the uptake of nutrients into the plant from the soil
- Leaf biochemical alteration, or chemical processes in the leaf were altered in common rainforest plants
- Reduced plant transpiration
- Cellular respiration may increase or decrease but it is dependent on the plant species or oil type
Did you know that there have been over 3000 spills in the Amazon forest from the 2800 km of oil pipelines that run underneath it? These spills have affected the wildlife and most of all the plants in the vast areas where there have been accidents, the plants there are now suffering from the effects stated above.
Effects of Sodium Chloride on General Plants
Sodium chloride is a chemical compound that the human body needs to maintain a regular fluid balance. All natural waters have some amount of sodium chloride usually six to 130 ml per litre. For humans, too much sodium chloride can lead to heart disease, stroke, or high blood pressure.
This subject in the experiment represents if a home gardener decided to give their radish plants tap water. The results of this experiment will be helpful to this group of people.
These are some of the effects of sodium on general plants:
- Root exposure to high amounts of sodium stunts growth due to excess salts
- Hinders water uptake - Therefore this will lead to dry tissues
This chemical may lead to the death of sensitive and fragile plants.
Effects of Coconut Milk on General Plants
Coconut milk is a liquid that has many different chemicals and nutrients in it. Below is a list of nutrients and chemicals in coconut milk per 240 g or approximately one cup of coconut milk:
- 631 mg potassium
- 88.8 mg magnesium
- 38.4 mg calcium
- 13.3 mg carbohydrates
- 5.5 mg protein
- 57.1 mg fat
This experiment will not be testing each of these chemicals as an individual on the plant but coconut milk as a whole. This liquid is a key part of tropical Asian culture and the origin of using it as a fertilizer for plants. This subject in the experiment tests the effect of this seemingly clever fertilizer on specifically radishes. This fertilizer is also used by many home gardeners as it seems to have a positive effect on most plants.
The clever part of this fertilizer is that it is not hard to find as you can find this liquid in many grocery stores and it is rich in potassium which is a key nutrient that many plants need.
Variables
Controlled Variables
- The air temperature in the room of the plant
- Amount of liquid given to it every day
- Amount of light received
- Soil
- External nutrients
- Type of radish ( Cherry Belle)
- Space of growth
Manipulated Variables
- Different chemicals in the water given to the plants
Responding Variables
- The growth of the plant
- The edibility of the plant
- The health of the plant
Procedure
1. Gather the needed materials for the experiment. ( Cherry Belle radish seeds, Gardening soil 28.3 liters, Compostable Jiffy pots, Fluorescent light, Soil scoop, Measuring cup, Coconut Milk, Hydrocarbon, bottled water, salt, Syringe, Shower(not a bathtub), extension cord) Make sure coconut milk is refrigerated.
2. Fill all eight pots with the same amount of soil, all the way up to the brim of the pots, determine this using the measuring cup. (control, coconut milk, hydrocarbon, sodium chloride x2)
3. Set up the light over the shower bench so facing downwards then place pots up
4. Use the soil scoop to dig a small hole, about 1.5 cm deep.
5. Place two Cherry Belle Radish seeds in each hole.
6. Cover up the hole using the soil scoop
7. Water the eight radish plants 30 ml or 1/8 cup per 5 days in addition to 1.5 ml of the manipulated variable based on the respective test subject or radish plant every day until four weeks and two days or 30 days have passed since you first planted the plant. Use the syringe to add the manipulated variable to the water.
8. Observe the final result
Observations
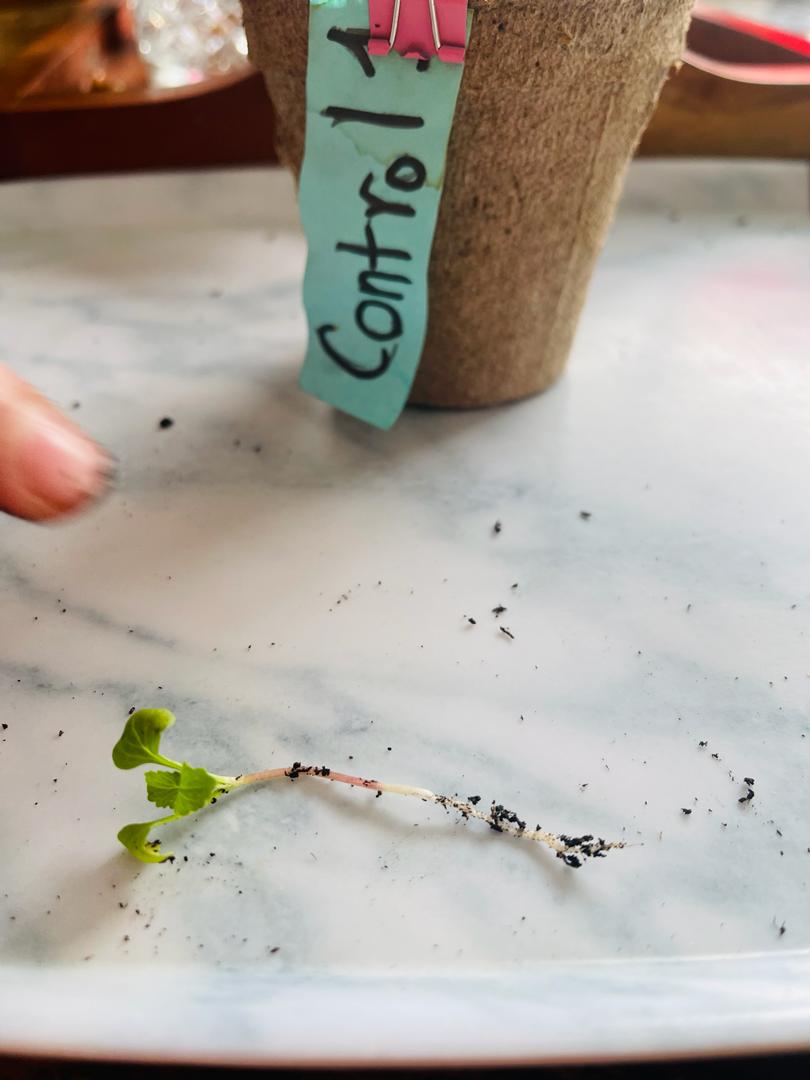
Control 1
- This plant has three main leaves, each 1.5 cm wide and 1 cm tall
- 4 cm taproot
- Also no red bulb but there is a spot that is a maroon colour and that is where it would have grown
- Rich healthy green leaves
Control 2
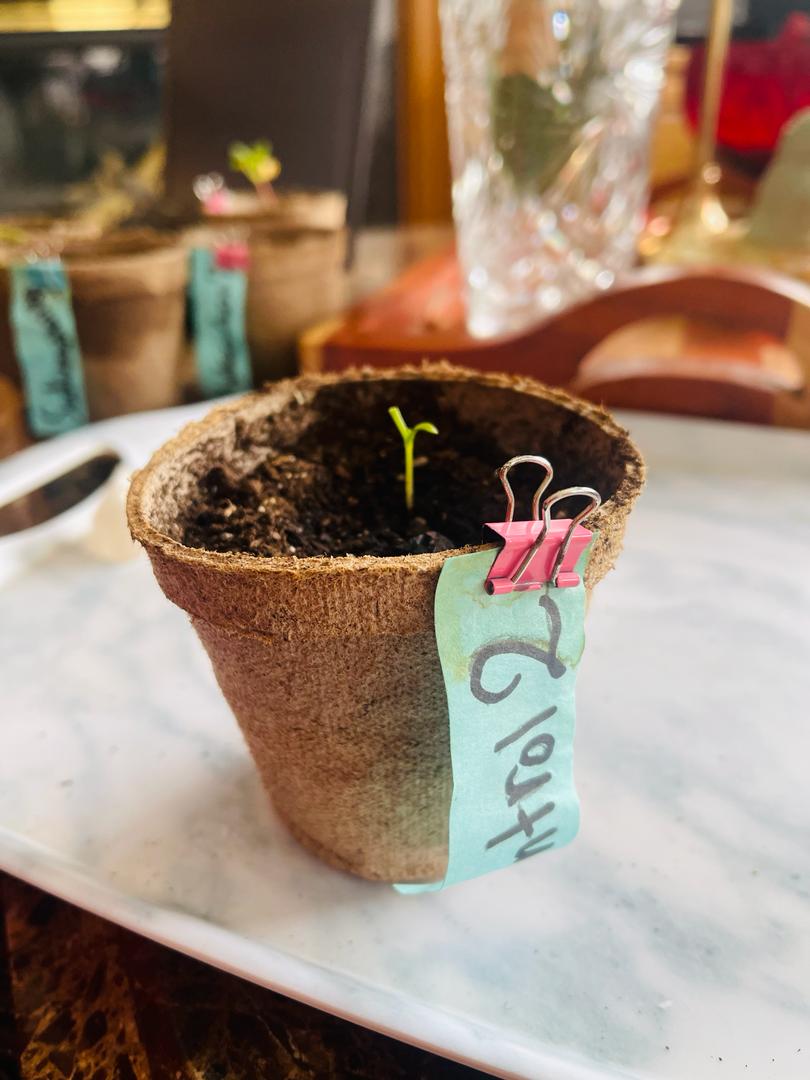

- No radish bulb
- There was a section of the stem that was the maroon color of a bulb
- 1 cm above the dirt
- Two 3 mm leaves sprouting out of the stem
- 2 cm taproot
Sodium Chloride 1
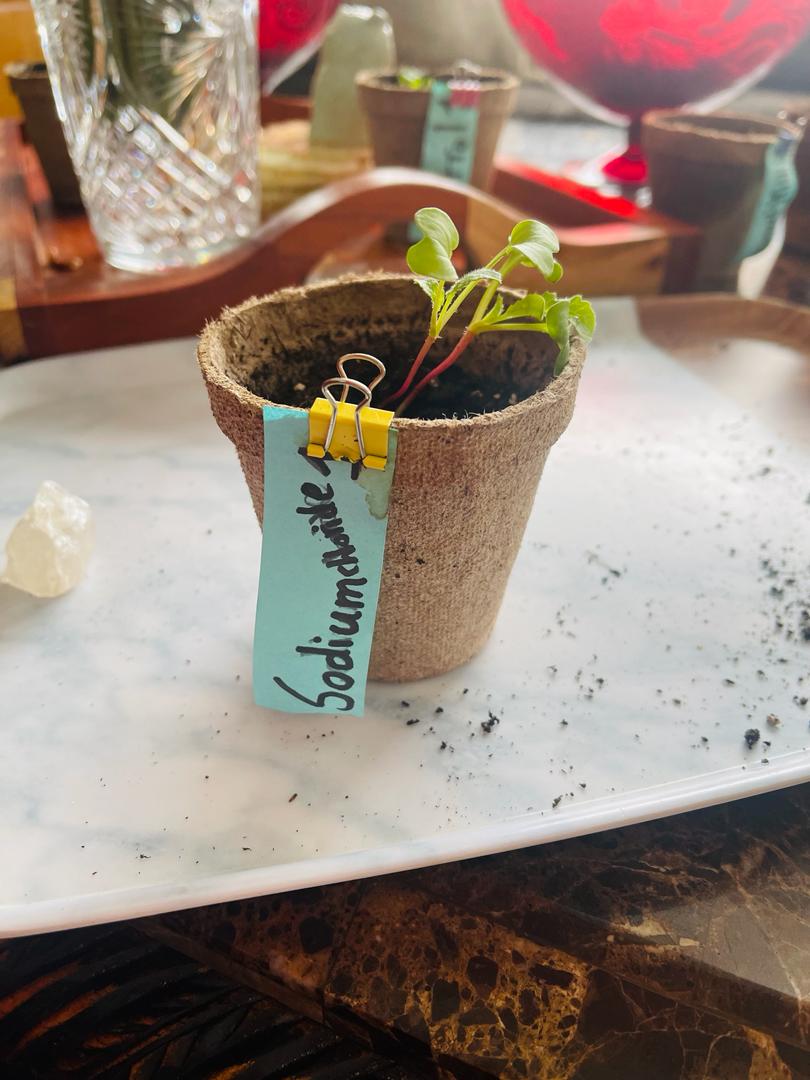

Healthy plant compared to others and counterpart
- Two main stems sprouting out
- Same-sized leaves as control 2
- 8 leaves - all a healthy green
- Somewhat weak root and stem
Sodium Chloride 2
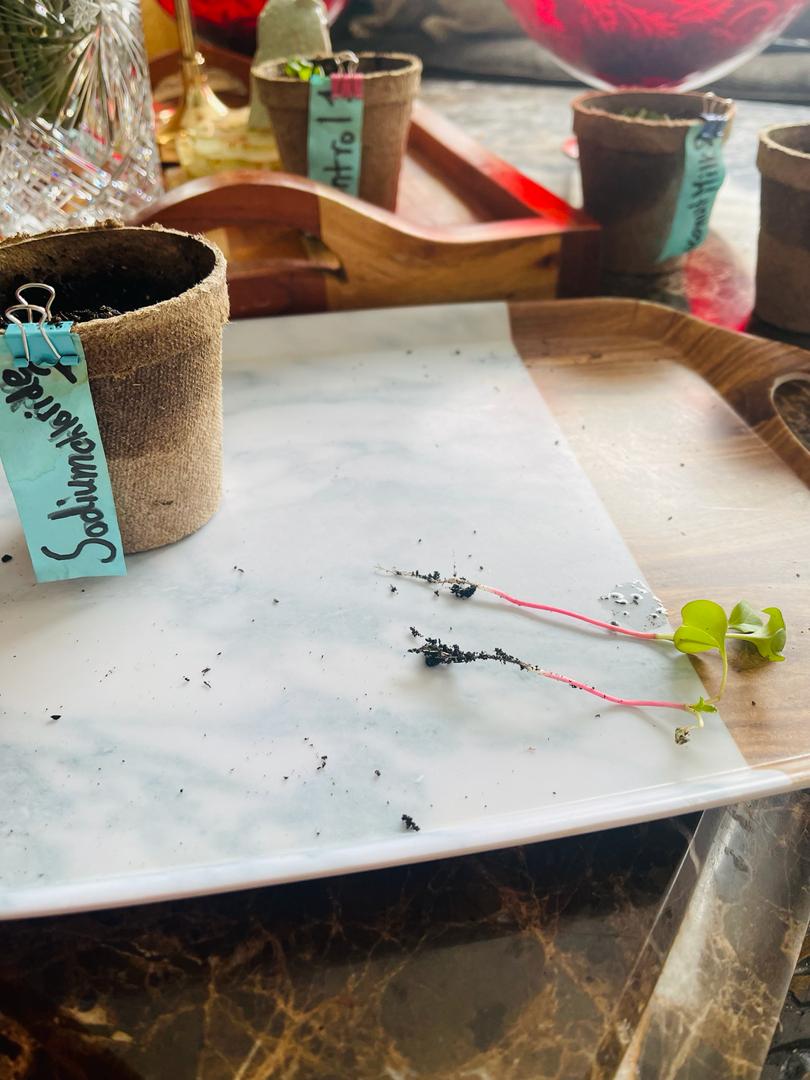

- Grew taller by 2 cm than its counterpart
- Two plants grew but one had extremely small leaves and an abnormally weak stem
- The second plant had 3 healthy leaves sprouting out of its stem
- The leaves on the second plant were 0.76 cm bigger than the other
- The second plant had a longer taproot by half of a cm
Hydrocarbon 1
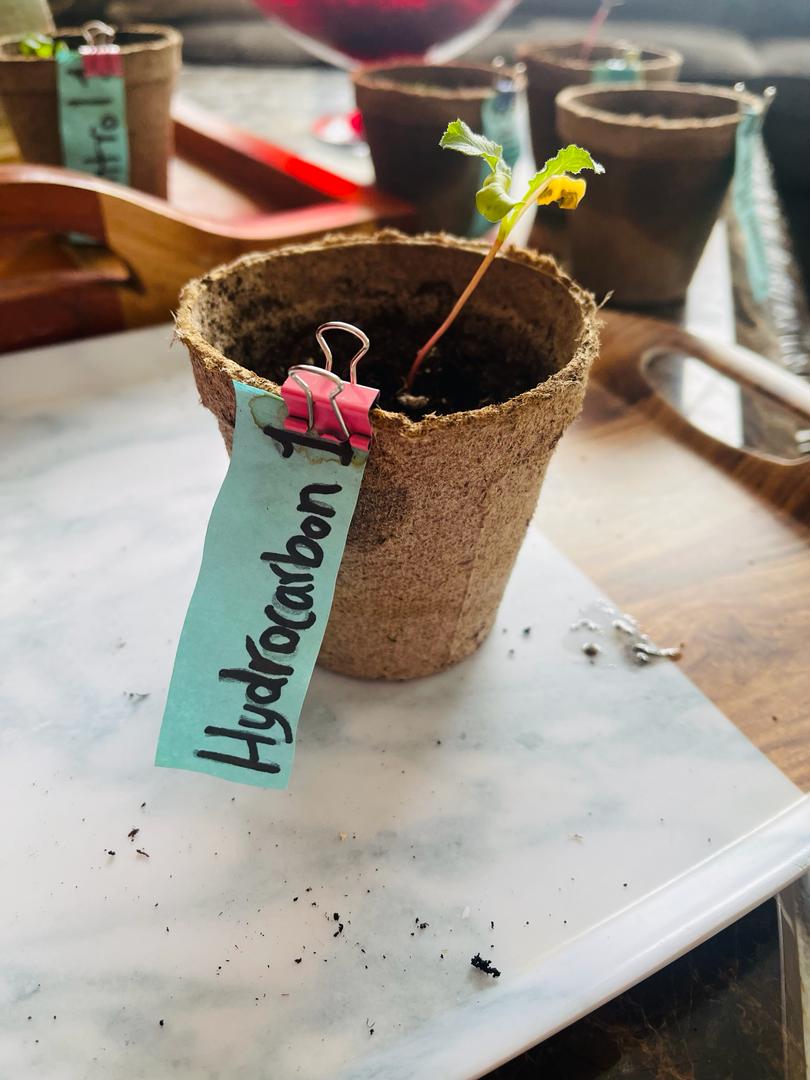

- Grew 7 cm above soil level
- 4 leaves sprouted out of its stem
- Dry and wispy leaves
- 3cm taproot
- root is well established in the soil
- Leave are frail and very light green color
Hydrocarbon 2
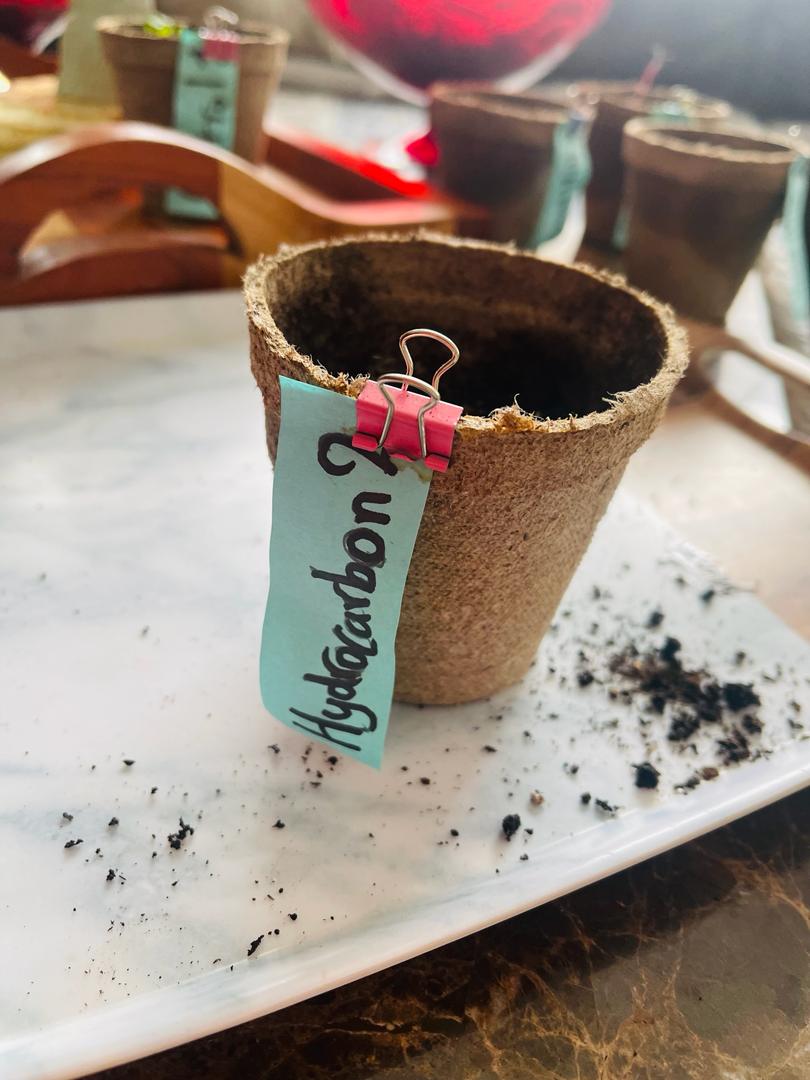

- This plant did not germinate
- Further investigation showed that about 2 mm of the root had developed downwards
- Radish has an 80% germination rate so this blunder could be a matter of probability
Coconut Milk 1
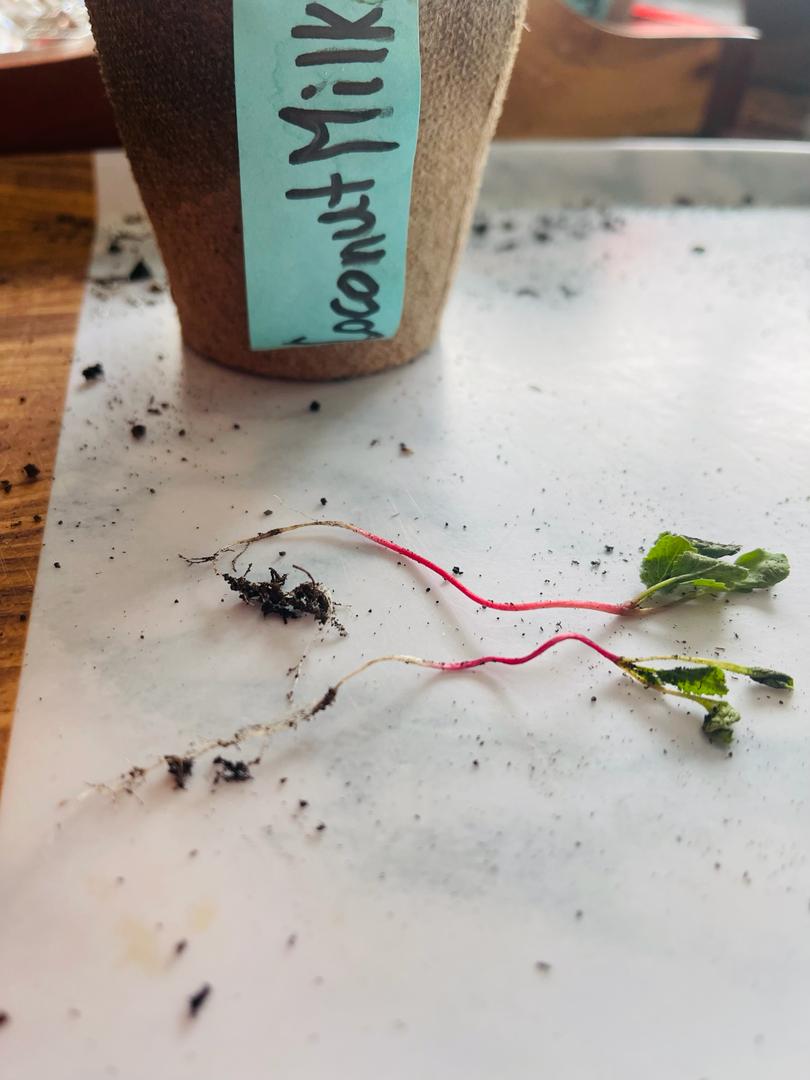

- Extremely weak stem
- Dry, wispy leaves
- Though the root was long it was not well developed inside the soil as most of the root was stationed in one specific spot rather than branching out into the depths of the soil
- The second plant or the plant closest in the picture's leaves were not well developed
- One plant had 2 leaves sprouting out of its stem whereas the other had three as they were not well developed
Coconut Milk 2
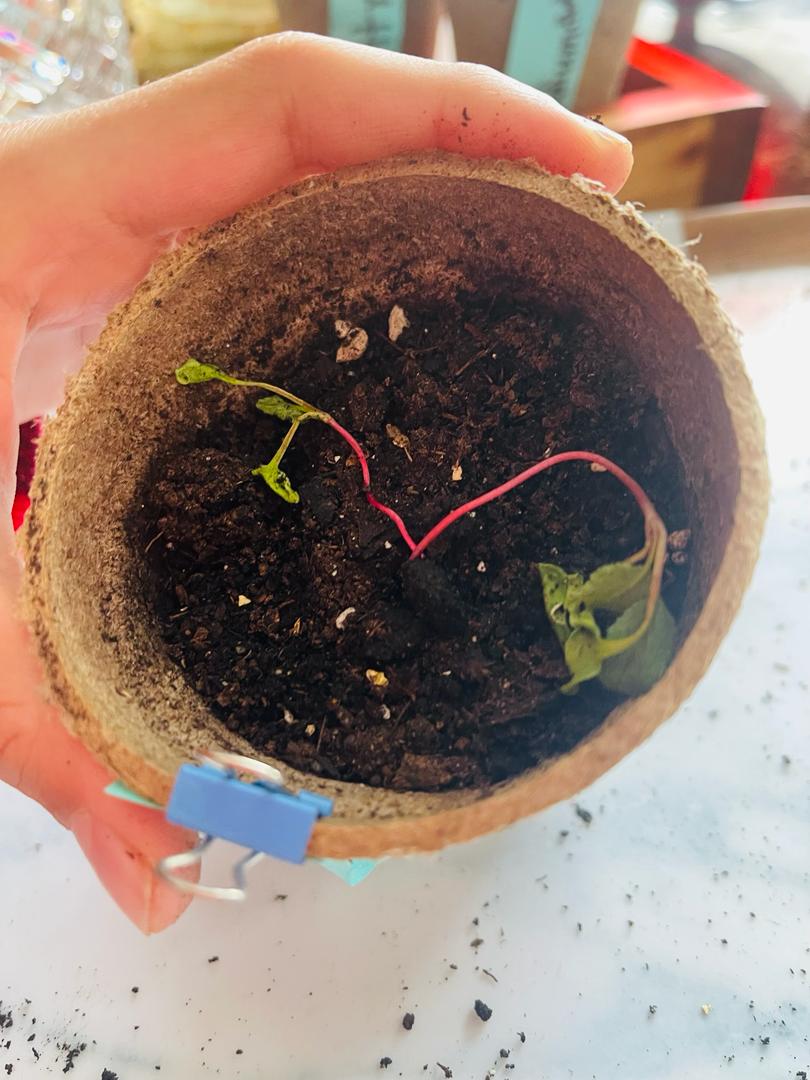

- This plant's stem was also extremely weak
- Stem could not hold the whole plant up as you can see in the photo
- Again one plant's leaves were well developed though frail, wispy and dry and the other's not grown and still had the same characteristics
- 3 leaves sprouting out of each plant's stem
- The plant on the right was 1cm taller
- Right plant: 6cm
- Left plant: 5cm
Analysis
Expected results
Although the radish bulbs would make a significant difference in our findings and would increase the functionality of this experiment, we can still interpret the manipulated variable's effects on the plant by analyzing its stem, leaves, and root to further build upon our understanding of this topic.
The expected results would align with the research section where the effects of the substances used as manipulated variables on general plants were stated. This would include the plant given coconut milk thriving and the other plants not growing to their full potential due to the harmful chemical. Although the results were not extremely far from these narratives, there were some unexpected bloomers.
The radish bulbs did not grow for all plants due to section five of the procedure, stating that the scientist experimenting should place precisely two radish seeds in each hole that was made in the step before this. This caused competition for water and nutrients between the plants, resulting in plants not growing to their full potential. Although this may have changed the results, this was a controlled variable in some sense as it was the same for all plants, this means that the plant's growth may have decreased, but all plants' growth changed the same amount hence our qualitative results are accurate and the quantitative observations can be calculated to match that of one seed in each hole in ratio form. As a result of this unexpected blunder, the edibility of the plant can no longer be tested accurately. This is also why in many pots only one plant germinates
Analysis Specific to Plant
Note: Please keep in mind the problem mentioned above during all and specifically this section of the Analysis
Controls 1 and 2
These plants are regular radish plants without disturbance to their water. Again the plants did not grow as well due to the mistake of placing two seeds causing the plants to compete for nutrients and water.
Sodium Chloride 1
This plant was healthy despite its weak stem. I believe that the weak stem was a result of the salt in the soil. The excess salt led to drier tissues, in this case the stem. This was a successful plant but it had shown unmistakable signs of being able to grow more, an example of this could be the smaller leaves that were starting to develop and the more recent outbursts of petiole that could have led to more leaves.
Sodium Chloride 2
In this pot 2 plants sprouted out, one of them, grew taller by 2 cm than its counterpart. This is due to the other plant not competing well for water and nutrients, hence the abnormally weak stem and extremely small and undeveloped leaves. The undeveloped leaves could also result from this certain plant taking in more of the salt given to the two plants through its phloem. The plant that fared better had three healthy leaves larger than its counterpart(Sodium Chloride 1). This plant also had a longer taproot which is the primary reason why this plant grew well, as the plant did not have to compete in just one area but could reach lower for extra nutrients and hydration.
Hydrocarbon 1
In this pot, only one plant sprouted out, again due to the problem of two seeds in one hole. This plant had dry and wispy leaves. This aligns very accurately with the substance's effect on general plants. These dry tissues could be the result of the substance altering the chemical process in the plant, in this case, respiration. This chemical also causes reduced transpiration which is another reason that may account for the dry, wispy characteristics of the plant's leaves.
Hydrocarbon 2
This plant or these plants did not germinate. This was not stated in the research as I believe it is a new find. Although this could be undiscovered, the matter of probability shouldn't be forgotten. As the germination rate of radishes is not 100%, as is no natural seed.
Coconut Milk 1
In this pot, two plants grew. Similar to the second sodium chloride plant, one plant had undeveloped, dry leaves. The second plant had 2 healthy leaves sprouting out of its stem. A difference that was unique to this plant and its counterpart specifically was their abnormally weak stem. The two plants could not stand up.
Coconut MIlk 2
Similar to the other coconut milk test subject, this plant's stem was abnormally weak and it would not stand up to its full height. We can infer that this is an effect of coconut milk on the cherry belle radish plant as it was a similar common characteristic of the two plants that were given coconut milk in their water.
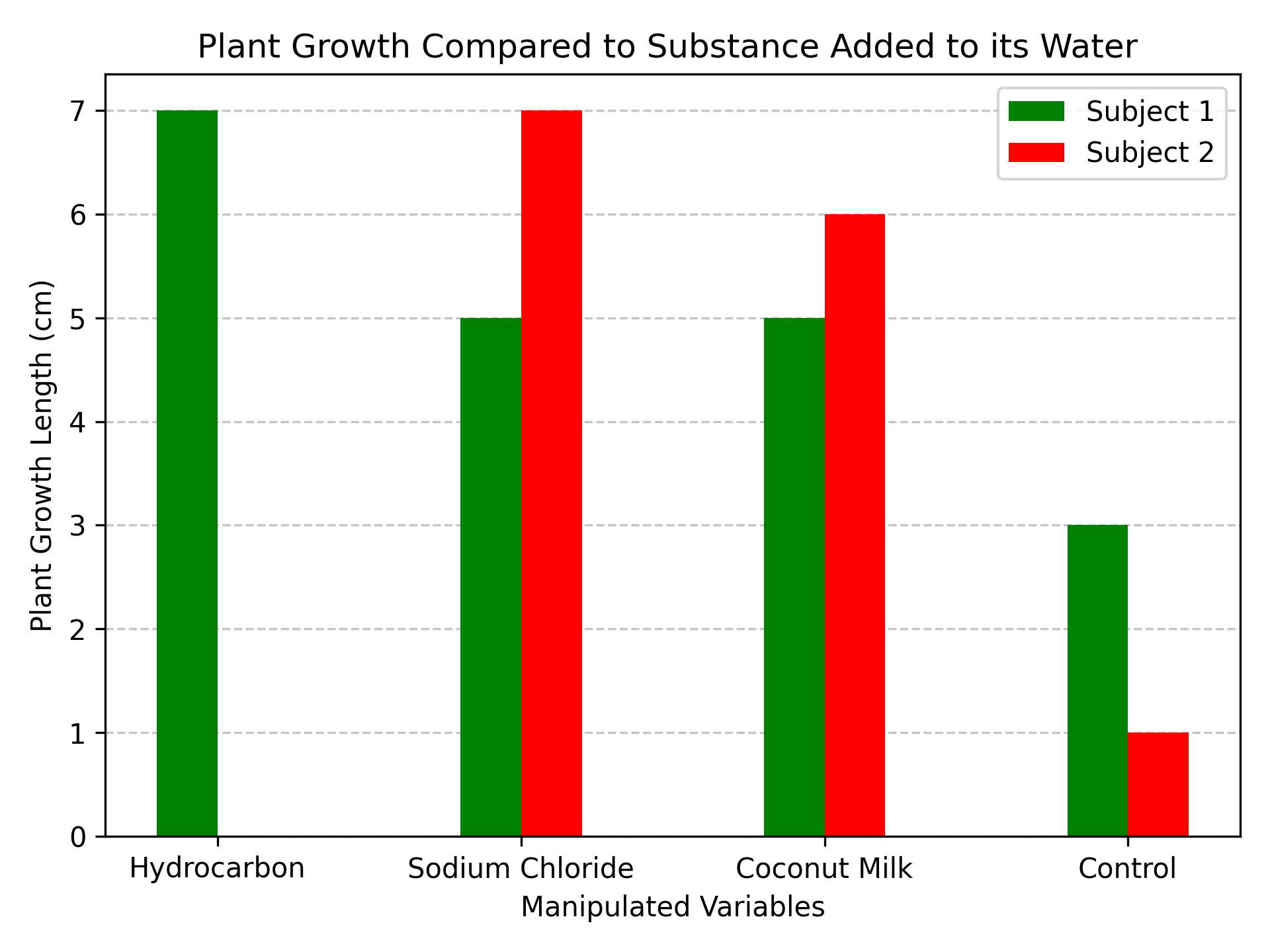
Note: The reason that the second hydrocrabon plant's bar is non-existent is as that plant did not germinate(This graph is representation of groth above the ground)
This graph is visual representation of the height of the plants. Although this shows the length of the plant, due to the abnormally weak stem of some plant caused by their unique manipulative variable, some plants may not be standing up to their full length. Also keep in mind that this chart shows the maximum value of the two plant that may or may not have grown.
Predictions if Radish Bulbs had Grown
I believe that the radish bulb had grown some of them would be unsafe to eat for example the plant with hydrocarbon in its soil and water. The equivalent of this without a radish logically would be drinking petroluem. Futher research shows that if this chemical finds its way to a human body's lungs, it can cause incurable and permanent lung damage and even death. Certain types of hydrocarbons can cause seizures, coma, damage to the kidney and liver.
I believe that the radish bulb would have diluted the effect of this substance yet it would still cause the less sigmificant of the list of possible effects. This could mean seizure, coma or irregular heart beats.
The test subjects with sodium chloride and coconut milk might taste strange but unless taken in extremely large amounts, would not have any significant changes to one's health. These manipulated variables might just make the radish taste similar to themselves.
Conclusion
Reviewing this experiment, many of the plants could not grow to the standards set by others. Pairs of plants did have similar characteristics so we can infer that the manipulated variables did alter the results of the experiment. The plant that thrived the most would have been sodium chloride subject two. Other plants did reach the same heigh as this plant but the main reason this plant is at the top is due to both seeds in the pot growing despite the error of planting two seeds in one 1.5 cm deep hole in the soil. On top of this, the plant's leaves were not dehydrated, but a rich green and a large size.
In the hypothesis, I predicted that the control would grow best, though I also refered to my hypohesis having a chance of being incorrect as any manipulated variable could have acted as a fertilizer. Looking back my hypothesis was incorrect as the control plants did not grow as well as some others.
We can accurately infer the effects of the manipulated variables, taking in mind the characteristics that both plants had. The coconut milk caused a weak stem as both plants grew to a satisfactory height though neither were standing up as others were. Though this substance might have effected the stem, the leaves of these plants were normal considering the mistake mentioned above as this caused competition for water and nutrients. The hydrocarbon caused dry tissues, especially in the leaves. I noticed that further the hydrocarbon prevented this plant from being hydrated as it was not transpirating as much as other plants. We have evidence that this is the effect of this substance as it aligns with what was discovered previously, noted in the research sectiorn. Finally the sodium chloride, or salt caused no particular change as the stem and leaves were as very similar to the control plants yet they grew a significantly larger size. Although I am skeptical of this result, evidence shows that salt had a positive effect on the plant though this does not align with the research as sources state that salt brings excess minerals to the soil.
If the radish bulbs had grown, two of the three pairs of test subjects would have been safe to eat though the hydrocarbon test subjects would not. This substance can be a potentially deadly poison as it can cause irreversable and permanent lung damage which could lead to death. Depending on the type of the oil, other negative side effects could take place. This is further reason why industrial farming companies should be wary of their farming grounds.
If someone were to repeat this experiment, these are some suggestions:
- Plant one seed in each hole while planting
- Have an autonomous watering system.
- Give radish plants sufficient spacing in larger pot
Further topics to investigate following up on this experiment could be doing tests similar to this on a smaller scale, perhaps testing a simgle chemical that is plentiful in farming land. Though this could be useful for farming, an important topic to further research is the effects of these chemicals on the bulbs of the radish as in this experiment we were not able to test this but make relatively accurate predictions. On top of this due to the flexibility of the manipulated variables and the controlled variables such as the type of plant, this can easily be optimized as a mandatory test before planting anything in bulk.
Application
This project is based on farming, life science, environmental science, plant science, pollution on the ground, and botany. In this project, I added different chemicals to the water given to the plants to observe the effect on the plant itself, specifically on its growth and edibility. The results of this project can be of use to farmers who want to plant radishes, either on their farms or in Canadian homes ( See Subject 3). Specifically knowing the effects of the chemicals in the ground or some cases in the water given to their plants. In cases where they are growing this plant in very large amounts for commercial purposes, not knowing the effect of the chemicals in the ground or the water given to them can lead to very large-scale accidents which may cause hundreds of thousands of dollars lost that can even result in the end of a company. One of the manipulated variables in this experiment was hydrocarbons added to the water given to the plant. Hydrocarbons are the base of petroleum which is one of the world's most used energy sources. The use of this source worldwide can lead to accidents in which the information in this project will be very valuable. Another manipulated variable in our experiment was sodium. This is a chemical that is found naturally in all waters and our drinking water. This part of the experiment will be helpful to people who water their radishes at home using their drinking water. The last variable in this experiment was coconut milk which is a liquid that is easy to find and it was shown to have a positive effect on most plants as it is rich in potassium a key nutrient needed by many different species of plants. In addition to knowing the effects of these chemicals on radishes, people also now looking at this project can test their chemicals based on their situation.
Sources Of Error
Although many errors changed the results of the experiment, planting two seeds in one hole effected the results the most. This caused competion for nutrients and water, also not giving the radish plant sufficient space to grow it's bulb. This significantly narrowed down our range of results that would have been extremely relevant and useful.
Another error that also changed the plants was giving them bottled water. The Pure Life company owned by Nestle uses reverse osmosis to filter their water. This is the process of applying pressure to contaminated water causing it to pass through a membrane hence minerals and contaminants are left behind. Minerals are something essential for plants and by giving the plants what I though was a controlled variable, I decreased their range of growth. I am not suggesting the use of tap water but a controlled and knowledgable source of water with optimal amounts of minerals.
Other issues can include:
- The use of artificial sunlight or growlight
- Movement of the plants to different locations in the midist of the experiment
- The use of jiffy pots(Did not give radish sufficient space, would recommend larger pot)
Citations
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). How to write a strong hypothesis: Steps & examples. Scribbr. https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/hypothesis/
Services, E. A. (2023, August 4). What is and how to write a good hypothesis in research?. Elsevier Author Services - Articles. https://scientific-publishing.webshop.elsevier.com/manuscript-preparation/what-how-write-good-hypothesis-research/
Library: Guide to Research and Writing for the Academic Study of Religion: Preliminary research. (n.d.). https://libguides.ucalgary.ca/c.php?g=707494&p=5035567
Haider, F. U., Ejaz, M., Cheema, S. A., Khan, M. I., Zhao, B., Cai, L., Salim, M. A., Naveed, M., Khan, N., Núñez‐Delgado, A., & Mustafa, A. (2021). Phytotoxicity of petroleum hydrocarbons: Sources, impacts and remediation strategies. Environmental Research, 197, 111031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111031
Managing Pests in Gardens: Vegetables: Cultural tips for Growing radish. (n.d.). https://ipm.ucanr.edu/home-and-landscape/radish/cultural-tips/index.html?src=307-pageViewHLS#:~:text=Radishes%20can%20be%20grown%20from,growing%20season%20for%20continuous%20harvest.
Radish. (n.d.). https://www.smartgardener.com/plant/50-https://ipm.ucanr.edu/home-and-landscape/radish/cultural-tips/index.html?src=307-pageViewHLS#:~:text=Radishes%20can%20be%20grown%20from,growing%20season%20for%20continuous%20harvest.
Managing Pests in Gardens: Environmental Factors: Nutrient and mineral excesses, salinity, and salt toxicity—UC IPM. (n.d.). https://ipm.ucanr.edu/PMG/GARDEN/ENVIRON/salttoxicity.html#:~:text=Sodium%20may%20damage%20roots%20through,water%20needed%20for%20plant%20growth.
Measurement equivalents | Exploratorium. (2023, August 29). Exploratorium. https://www.exploratorium.edu/food/measurements
Miller, C. (2020, September 1). 3.3 biochemical compounds. Pressbooks. https://jwu.pressbooks.pub/humanbiology/chapter/3-3-biochemical-compounds/#:~:text=Biochemical%20compounds%20are%20carbon%2Dbased,molecules%2C%20which%20are%20called%20monomers%20.
Pure water can KIll you. (2015, January 9). I, Science. http://isciencemag.co.uk/features/fact-of-the-day-1/
Growing radishes in home gardens. (n.d.). UMN Extension. https://extension.umn.edu/vegetables/growing-radishes#:~:text=Radish%20taproots%20can%20be%20large,flavor%20and%20a%20tough%20texture.
Vinje, E. (2023, August 6). Growing radishes: How to plant, grow, and harvest radishes. Planet Natural. https://www.planetnatural.com/growing-radish/#:~:text=radishes%20for%20weeks.-,Light,growing%20leaves%20rather%20than%20roots.
Fernando, J. (2023, July 15). Hydrocarbons: definition, companies, types, and uses. Investopedia. https://www.investopedia.com/terms/h/hydrocarbon.asp
Grifoni, M., Rosellini, I., Angelini, P., Petruzzelli, G., & Pezzarossa, B. (2020). The effect of residual hydrocarbons in soil following oil spillages on the growth of Zea mays plants. Environmental Pollution, 265, 114950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114950
Rahbar, F. G., Kiarostami, K. H., & Shirdam, R. (2012). Effects of petroleum hydrocarbons on growth, photosynthetic pigments and carbohydrate levels of sunflower. Journal of Food Agriculture & Environment, 10, 773–776. https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/abstract/20123098898
Arellano, P., Tansey, K., Balzter, H., & Boyd, D. S. (2015). Detecting the effects of hydrocarbon pollution in the Amazon forest using hyperspectral satellite images. Environmental Pollution, 205, 225–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.05.041
Alexandrapopescu. (2023, September 12). Hundreds of oil spill sites threaten Amazon Indigenous lands, protected areas. Mongabay Environmental News. https://news.mongabay.com/2023/09/hundreds-of-oil-spill-sites-threaten-amazon-indigenous-lands-protected-areas/
Sodium — Middlesex-London Health Unit. (n.d.). https://www.healthunit.com/sodium-in-drinking-water
Health Canada. (2012, April 25). Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water quality: Guideline Technical Document – Sodium. Canada.ca. https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/publications/healthy-living/guidelines-canadian-drinking-water-quality-guideline-technical-document-sodium.html
Salt and sodium. (2023, June 13). The Nutrition Source. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/salt-and-sodium/#:~:text=But%20too%20much%20sodium%20in,more%20than%20our%20bodies%20need.
Library Research Guides: STEM: How to write a lab Report. (n.d.). https://guides.libraries.indiana.edu/c.php?g=992698&p=7182653
Hydrocarbons: the deadly poison found in everyone’s home. (2016, December 27). Connecticut Poison Control Center. https://health.uconn.edu/poison-control/about-poisons/cleaning-products/hydrocarbons-the-deadly-poison-found-in-everyones-home/#:~:text=When%20a%20hydrocarbon%20gets%20into,lung%20damage%3B%20and%20even%20death.
Acknowledgement
Thank you to my parents for supplying me with materials I needed and keeping me going. Also thank you to my science fair coordinator who gave me the chance to participate in this wonderful oppurtunity.