Sunscreen and it's Affects
Grade 8
Presentation
No video provided
Hypothesis
Partner 1 :I hypothesize that the different sunscreen will look different on the UV paper and that the Neutrogena sunscreen will perform the best.
Partner 2: I hypothesize that banana boat will be the best on the Uv paper , as it's a chemical sunscreen, so the chemicals will block the UV rays from reaching the paper.
Research
What is sunscreen?
Sunscreen,also known as sun block, is a cream/lotion that is regularly applied to the skin during the times of extreme heat, to prevent UV rays damaging the skin.
History of sunscreen
Benjamin Greene, a pharmacist, developed a gelatinous substance for sunscreen, supplied to soldiers during World War II. Schueller and Greiter, chemists, developed the first sunscreen. Greene later founded Coppertone, introducing sun protection factor in the 1960s.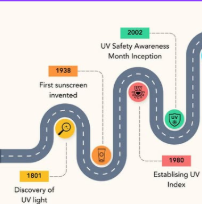
What does SPF stand for?
Skin Protection Factor
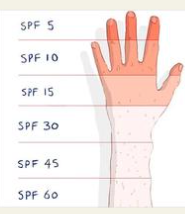
Whats better High or Low SPF?
The skin cancer foundation recommends using high-number SPFs for protection against UVB rays. High-number SPFs offer the same lifespan as low-number SPFs, but require reapplying. Wearing SPF 15 sunscreen daily can reduce melanoma and SCC (Squamous cell carcinoma) risk by 50% and 40%, respectively.
Types of sunscreen
Chemical blockers contain chemicals that absorb the sun’s ultraviolet rays. Physical blockers , also known as mineral blockers, have one of two active ingredients—titanium dioxide or copper oxide—and scatter UV radiation from the sun.


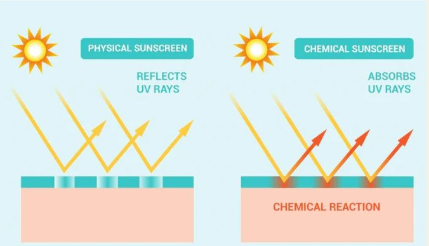
Is sunscreen harmful?
Some researchers claim that a dangerous mixture of hazardous substances in sunscreen may be the cause of skin cancer. Sunscreen is ineffective to cautions that it is dangerous are examples of assertions.
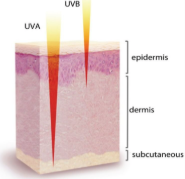
How do sun rays affect the skin without sunscreen?
There are 3 layers of the skin. The epidermis is the top layer , the dermis is the inner layer connecting the epidermis and subcutaneous. The subcutaneous is the lowest layer of the skin. UVB can harm skin cells and can cause dna mutations sometimes leading to types of skin cancer like melanoma. UVA damages skin leaving you with a tan. When the epidermis (the top layer of skin) is exposed to the sun unprotected it prematurely ages the skin.
Q: Does employing sunscreen increases your chance of developing a vitamin D deficiency?
Sunscreen does, in fact, prevent UVB rays, which are shortwave radiation from the sun that are crucial for the skin's production of vitamin D.
However, users are usually not vitamin D deficient because most individuals apply much less sunscreen than is advised (approximately a teaspoonful for the face and a shot glass-sized amount for the body).”
Onzone layer
The ozone layer protects living beings from being exposed to too much ultraviolet rays which could cause severe injuries. Neither plant life nor human life can survive or thrive without the ozone layer. Too much UV exposure can cause skin cancer and sunburn.
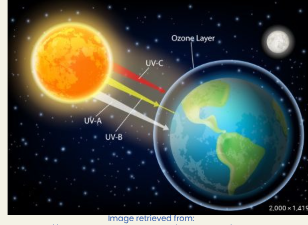
Understanding the distinctions between UVA, UVB, and UVC radiation.
UVA:
- The longest wavelength
- reaches deep into the layers of the skin
- causes ageing/wrinkling
- 400-315
UVB:
- Has large effects on the top layer of the skin
- Causes redness/burning/skin cancer
- 315-280 wavelength
UVC:
- The shortest wavelength
- absorbed by the ozone layer
- 280-200
The difference between sunscreen brands
- Neutrogena, a chemical sunscreen, that contains oxybenzone which is a chemical that absorbs the UV rays rather than reflects them away from the skin.
- La Roche Posay is considered as a mineral sunscreen, that has Titanium Dioxide which helps reflect UVA and UVB rays.
- Banana Boat is a chemical sunscreen that contains Avobenzone which absorbs harmful rays from the sun.
Variables
Independant Variable: The brand of sunscreen
Dependant Variable: The change in the UV papers color
Controlled Variable: The amount of time under the UV light as well as the type of paper
Procedure
We have purchased the UV light and the UV reactive paper. The steps to the experiement are:
- Step 1: Place the UV light in an area where no one can be harmed
- Step 2: Grab a 3 sheets of UV reaactive paper and place sunscreen on it. ( each having a different brand on it)
- Step 3: Place the UV reactive paper under the UV light.
- Step 4: Turn on the UV light then exit the area.
- Step 5: After 30 minutes, take pictures of the paper
- Step 6: Combine all pictures to show a time lapse
Observations
Our experiment will be conducted from March 23- April 5, so there will be no observation on the website, but there will be on the trifold.
Analysis
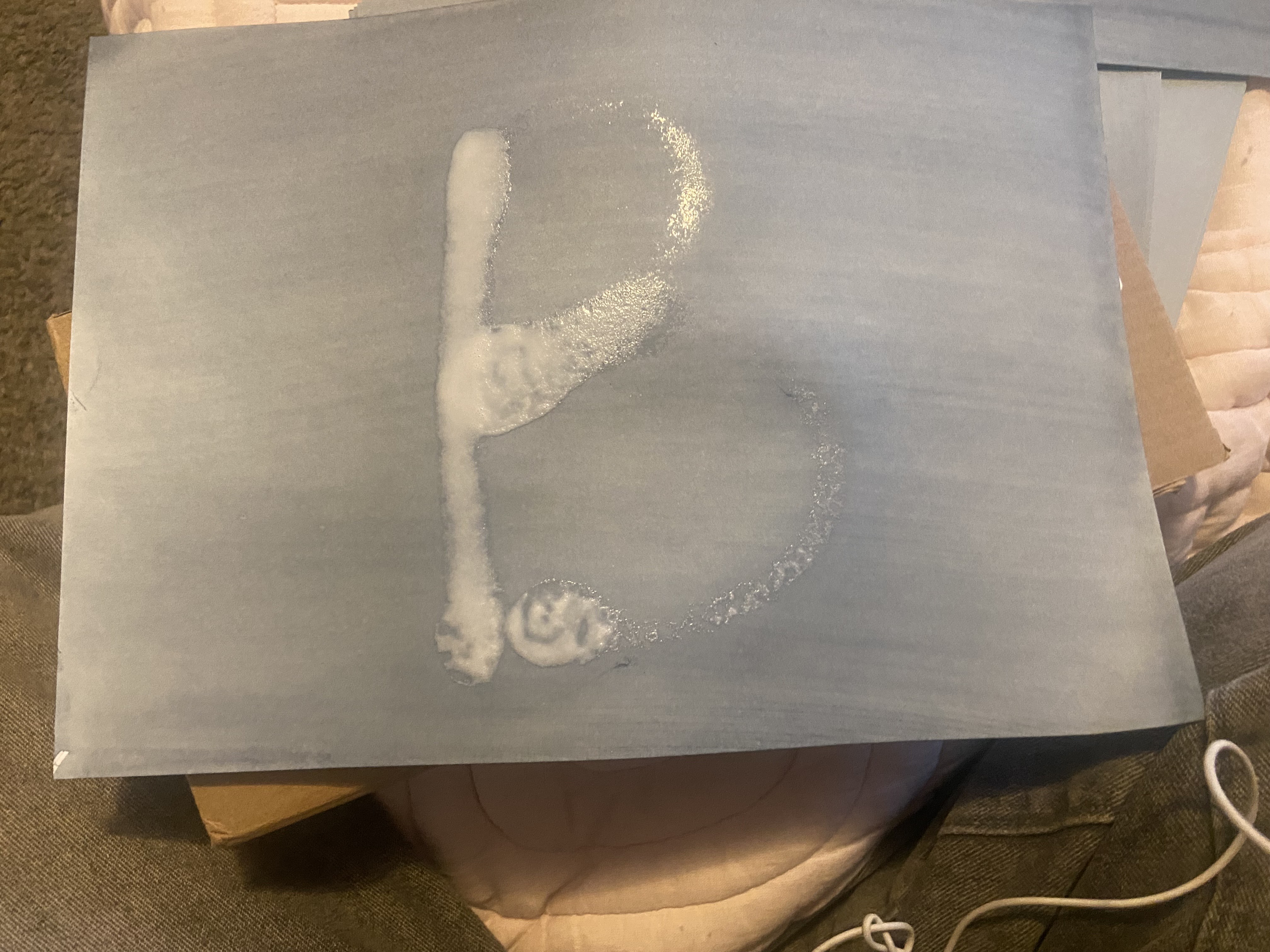



RESULTS:



Conclusion
In conclusion, sunscreen is good and bad at the same time. Sunscreen blocks UV rays, but not all are blocked. UV rays harm the skin and can cause skin cancer, and ageing. The most recommended sunscreen is La Roche Posey because it’s a mineral sunscreen. Mineral sunscreens are better because they don’t contain the chemicals in chemical sunscreen. Before purchasing sunscreen, make sure to check if it a mineral or chemical sunscreen because the chemicals sunscreen is worse than the mineral. As for the experimnet, we are still working on it, so the conclusion for it will be on the trifold.
Application
We bought UV reactive paper, then applied the different types of sun screen on them. Then we left them udner the UV lights that we purchased for an hour. We tested the following types of sunscreens: LA ROCHE-POSAY, Neutrogena, and Banana boat. We compared the paper that was left under the UV lights to the original paper that came from the packaging to see how it was affected, and how the sunscreen helped protect its surface. We then wet the paper and waited for it to dry to see the results.
Sources Of Error
We tried this experiment before, but with regular paper. There was no difference on the paper, no matter how long you keep it under the UV light. So we decided to use UV reactive paper, and now we are waiting for the results. (when completed, results will be on the trifold)
Citations
- Drissi, Madeeha, et al. “Sunscreen: A Brief Walk through History.” Baylor University Medical Center Proceedings, vol. 35, no. 1, 1 Sept. 2021, pp. 1–3, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8682817/, https://doi.org/10.1080/08998280.2021.1966602.
- CYSF, CYSF. “CYSF.” Cysf.org, 2024, platform.cysf.org/project/browse/. Accessed 4 Feb. 2025.
- Canada, Health. “Ultraviolet Radiation.” Www.canada.ca, 29 Oct. 2019, www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/health-risks-safety/radiation/types-sources/ultraviolet.html.
- Skin Cancer Foundation. “Sunscreen - the Skin Cancer Foundation.” The Skin Cancer Foundation, The Skin Cancer Foundation, July 2022, www.skincancer.org/skin-cancer-prevention/sun-protection/sunscreen/.
- Harvard University. “Search - Harvard University.” Harvard University, 26 Feb. 2021, www.harvard.edu/search/?q_as=sunscreen. Accessed 4 Feb. 2025.
-
- American Academy of dermatology Association. “Sunscreen FAQs.” Www.aad.org, 19 Oct. 2023, www.aad.org/media/stats-sunscreen.
Acknowledgement
We'd like to acknowledge our parents for helping us throughout the journey. They helped us non-stop, and we also helped eachother. We worked together as a team and that's how we've got 1st place at our school.

